NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane
- PMID: 24996901
- PMCID: PMC4195763
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201488147
NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane
Abstract
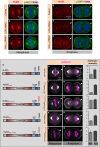
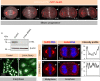
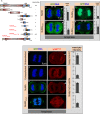
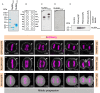
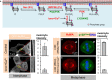
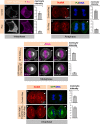
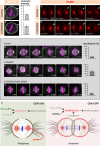
The positioning and the elongation of the mitotic spindle must be carefully regulated. In human cells, the evolutionary conserved proteins LGN/Gαi1-3 anchor the coiled-coil protein NuMA and dynein to the cell cortex during metaphase, thus ensuring proper spindle positioning. The mechanisms governing cortical localization of NuMA and dynein during anaphase remain more elusive. Here, we report that LGN/Gαi1-3 are dispensable for NuMA-dependent cortical dynein enrichment during anaphase. We further establish that NuMA is excluded from the equatorial region of the cell cortex in a manner that depends on the centralspindlin components CYK4 and MKLP1. Importantly, we reveal that NuMA can directly associate with PtdInsP (PIP) and PtdInsP2 (PIP2) phosphoinositides in vitro. Furthermore, chemical or enzymatic depletion of PIP/PIP2 prevents NuMA cortical localization during mitosis, and conversely, increasing PIP2 levels augments mitotic cortical NuMA. Overall, our study uncovers a novel function for plasma membrane phospholipids in governing cortical NuMA distribution and thus the proper execution of mitosis.
Keywords: NuMA; dynein; phosphoinositides; spindle elongation; spindle positioning.
© 2014 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NuMA phosphorylation by CDK1 couples mitotic progression with cortical dynein function.EMBO J. 2013 Sep 11;32(18):2517-29. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.172. Epub 2013 Aug 6. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23921553 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for dynein and astral microtubule-mediated cortical release and transport of Gαi/LGN/NuMA complex in mitotic cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Apr;24(7):901-13. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0458. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23389635 Free PMC article.
-
Ric-8A and Gi alpha recruit LGN, NuMA, and dynein to the cell cortex to help orient the mitotic spindle.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(14):3519-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00394-10. Epub 2010 May 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20479129 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NuMA in vertebrate cells: review of an intriguing multifunctional protein.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1137-46. doi: 10.2741/1868. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146802 Review.
-
NuMA after 30 years: the matrix revisited.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;20(4):214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.01.003. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20137953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spindle positioning and its impact on vertebrate tissue architecture and cell fate.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Oct;22(10):691-708. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00384-4. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34158639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polar relaxation by dynein-mediated removal of cortical myosin II.J Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 3;219(8):e201903080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201903080. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32497213 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the mechanisms of cell division.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 26;294(30):11382-11390. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AW119.008149. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31175154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynein-Dynactin-NuMA clusters generate cortical spindle-pulling forces as a multi-arm ensemble.Elife. 2018 May 31;7:e36559. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36559. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29848445 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity-dependent centrosome separation in the C. elegans embryo.J Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 2;218(12):4112-4126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201902109. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31645459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RA, Lovrien RE. Glycophorin is linked by band 4.1 protein to the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Nature. 1984;307:655–658. - PubMed
-
- Baines AJ, Lu HC, Bennett PM. The Protein 4.1 family: hub proteins in animals for organizing membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838:605–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

