Delivering nonidentical twins
- PMID: 24997601
- PMCID: PMC5417586
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2852
Delivering nonidentical twins
Abstract
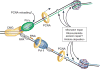
Two sibling DNA polymerases synthesize most of the eukaryotic nuclear genome. A new study provides insights into the distinct protein interactions that deliver these replicases for asymmetric leading- and lagging-strand replication and reveals possible cross-talk between DNA replication and other cellular processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment on
-
Mechanism of asymmetric polymerase assembly at the eukaryotic replication fork.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Aug;21(8):664-70. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2851. Epub 2014 Jul 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24997598 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

