Revealing long noncoding RNA architecture and functions using domain-specific chromatin isolation by RNA purification
- PMID: 24997788
- PMCID: PMC4175979
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2943
Revealing long noncoding RNA architecture and functions using domain-specific chromatin isolation by RNA purification
Abstract
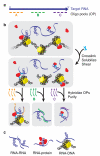
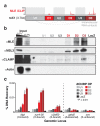
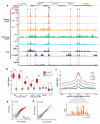
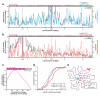
Little is known about the functional domain architecture of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) because of a relative paucity of suitable methods to analyze RNA function at a domain level. Here we describe domain-specific chromatin isolation by RNA purification (dChIRP), a scalable technique to dissect pairwise RNA-RNA, RNA-protein and RNA-chromatin interactions at the level of individual RNA domains in living cells. dChIRP of roX1, a lncRNA essential for Drosophila melanogaster X-chromosome dosage compensation, reveals a 'three-fingered hand' ribonucleoprotein topology. Each RNA finger binds chromatin and the male-specific lethal (MSL) protein complex and can individually rescue male lethality in roX-null flies, thus defining a minimal RNA domain for chromosome-wide dosage compensation. dChIRP improves the RNA genomic localization signal by >20-fold relative to previous techniques, and these binding sites are correlated with chromosome conformation data, indicating that most roX-bound loci cluster in a nuclear territory. These results suggest dChIRP can reveal lncRNA architecture and function with high precision and sensitivity.
Figures

Comment in
-
Non-coding RNA: Zooming in on lncRNA functions.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Sep;15(9):574-5. doi: 10.1038/nrg3795. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25048169 No abstract available.
-
Unraveling the lncRNA mystery.Nat Methods. 2014 Sep;11(9):890. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3089. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 25317457 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

