Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 24997849
- PMCID: PMC4201967
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-014-1314-y
Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
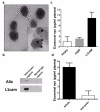
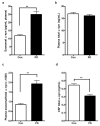
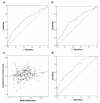
Extracellular α-synuclein is important in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) and also as a potential biomarker when tested in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The performance of blood plasma or serum α-synuclein as a biomarker has been found to be inconsistent and generally ineffective, largely due to the contribution of peripherally derived α-synuclein. In this study, we discovered, via an intracerebroventricular injection of radiolabeled α-synuclein into mouse brain, that CSF α-synuclein was readily transported to blood, with a small portion being contained in exosomes that are relatively specific to the central nervous system (CNS). Consequently, we developed a technique to evaluate the levels of α-synuclein in these exosomes in individual plasma samples. When applied to a large cohort of clinical samples (267 PD, 215 controls), we found that in contrast to CSF α-synuclein concentrations, which are consistently reported to be lower in PD patients compared to controls, the levels of plasma exosomal α-synuclein were substantially higher in PD patients, suggesting an increased efflux of the protein to the peripheral blood of these patients. Furthermore, although no association was observed between plasma exosomal and CSF α-synuclein, a significant correlation between plasma exosomal α-synuclein and disease severity (r = 0.176, p = 0.004) was observed, and the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity achieved by plasma exosomal α-synuclein were comparable to those determined by CSF α-synuclein. Further studies are clearly needed to elucidate the mechanism involved in the transport of CNS α-synuclein to the periphery, which may lead to a more convenient and robust assessment of PD clinically.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Cooper JM, Caballero C, Ferrer I, Obeso JA, Schapira AH. Chaperone-mediated autophagy markers in Parkinson disease brains. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(12):1464–1472. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(4):341–345. - PubMed
-
- Arai Y, Yamazaki M, Mori O, Muramatsu H, Asano G, Katayama Y. Alpha-synuclein-positive structures in cases with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: morphology and its relationship to tau aggregation. Brain Res. 2001;888(2):287–296. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Broadwell RD. Blood to brain and brain to blood passage of native horseradish peroxidase, wheat germ agglutinin, and albumin: pharmacokinetic and morphological assessments. J Neurochem. 1994;62(6):2404–2419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004696-5897/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004696/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES015459/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS082137/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065070/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG003156-30/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES016873/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES019277/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684-6221/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS085425/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033-6364/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

