Leveraging structure for enzyme function prediction: methods, opportunities, and challenges
- PMID: 24998033
- PMCID: PMC4117707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.05.006
Leveraging structure for enzyme function prediction: methods, opportunities, and challenges
Abstract
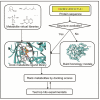
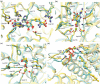
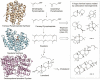
The rapid growth of the number of protein sequences that can be inferred from sequenced genomes presents challenges for function assignment, because only a small fraction (currently <1%) has been experimentally characterized. Bioinformatics tools are commonly used to predict functions of uncharacterized proteins. Recently, there has been significant progress in using protein structures as an additional source of information to infer aspects of enzyme function, which is the focus of this review. Successful application of these approaches has led to the identification of novel metabolites, enzyme activities, and biochemical pathways. We discuss opportunities to elucidate systematically protein domains of unknown function, orphan enzyme activities, dead-end metabolites, and pathways in secondary metabolism.
Keywords: docking; enzyme function prediction; homology modeling; metabolic pathways; protein structures.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein structure prediction and analysis as a tool for functional genomics.Appl Bioinformatics. 2003;2(3 Suppl):S3-10. Appl Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 15130810
-
Importance of molecular computer modeling in anticancer drug development.J BUON. 2007 Sep;12 Suppl 1:S101-18. J BUON. 2007. PMID: 17935268 Review.
-
Assignment of pterin deaminase activity to an enzyme of unknown function guided by homology modeling and docking.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Jan 16;135(2):795-803. doi: 10.1021/ja309680b. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23256477 Free PMC article.
-
From structure to function: methods and applications.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005 Apr;6(2):171-83. doi: 10.2174/1389203053545435. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005. PMID: 15853653 Review.
-
Prediction of protein function from protein sequence and structure.Q Rev Biophys. 2003 Aug;36(3):307-40. doi: 10.1017/s0033583503003901. Q Rev Biophys. 2003. PMID: 15029827 Review.
Cited by
-
The enzymatic nature of an anonymous protein sequence cannot reliably be inferred from superfamily level structural information alone.Protein Sci. 2015 May;24(5):643-50. doi: 10.1002/pro.2635. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25559918 Free PMC article.
-
QM/MM free energy simulations: recent progress and challenges.Mol Simul. 2016;42(13):1056-1078. doi: 10.1080/08927022.2015.1132317. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Mol Simul. 2016. PMID: 27563170 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of SgcJ, an NTF2-like superfamily protein involved in biosynthesis of the nine-membered enediyne antitumor antibiotic C-1027.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016 Oct;69(10):731-740. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.88. Epub 2016 Jul 13. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27406907 Free PMC article.
-
Chemometric Models of Differential Amino Acids at the Navα and Navβ Interface of Mammalian Sodium Channel Isoforms.Molecules. 2020 Aug 3;25(15):3551. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153551. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32756517 Free PMC article.
-
PCPD: Plant cytochrome P450 database and web-based tools for structural construction and ligand docking.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 24;6(2):102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2021.04.004. eCollection 2021 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33997360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot protein knowledgebase release 2014_01 statistics. [Online]. Available: http://web.expasy.org/docs/relnotes/relstat.html.
-
- UniProtKB/TrEMBL protein database release 2014_01 statistics. [Online]. Available: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/uniprot/TrEMBLstats.
-
- Friedberg I. Automated protein function prediction - the genomic challenge. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 2006;7:225–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

