Fluorescence Angiography with Temporary Occlusion to Confirm the Distal Artery: Technical Notes
- PMID: 24998630
- PMCID: PMC4628161
- DOI: 10.2176/nmc.tn.2013-0249
Fluorescence Angiography with Temporary Occlusion to Confirm the Distal Artery: Technical Notes
Abstract
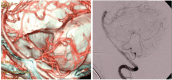
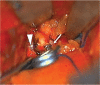
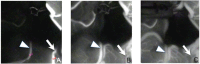
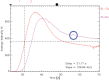
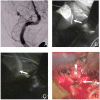
Confirming the patency of the proximal parent and distal artery is necessary in cerebral aneurysm surgery. To understand the relationship between the parent and distal arteries of the aneurysm, the blood vessels running through the subarachnoid space should be extensively dissected, which is time consuming. To examine the efficacy of a temporary clip with indocyanine green (ICG) technique, in which the parent artery is temporarily occluded using a temporary clip, an ICG videoangiography (ICGVAG) is performed to clarify the relationship between the distal artery and the proximal parent artery. Three patients with a distal aneurysm. This technique was used to confirm the connection of the parent and the distal artery in distal aneurysms. With regard to middle cerebral artery (MCA), the procedure is conducted as follows. First, the M2 within the Sylvian fissure is investigated to ensure the absence of atherosclerosis and perforators and that this vessel could undergo occlusion by temporary clipping. The subarachnoid space surrounding the distal artery of the lesion site suspected of an existent aneurysm is dissected. The image range of the ICGVAG is set sufficiently wide to accommodate the possibility that the distal artery is not the artery that was anticipated. Subsequently, after the temporary clip occlusion is completed, the ICGVAG is recorded. In the three distal aneurysms, the relationship between the aneurysm, the distal artery, and the parent artery was confirmed. This method was useful, suggesting that unnecessary dissection in the subarachnoid space might be reduced.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. All authors declare no personal interest in any of the materials or devices in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Dashti R, Hernesniemi J, Niemelä M, Rinne J, Lehecka M, Shen H, Lehto H, Albayrak BS, Ronkainen A, Koivisto T, Jääskeläinen JE: Microneurosurgical management of distal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Surg Neurol 67: 553– 563, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Horiuchi T, Tanaka Y, Takasawa H, Murata T, Yako T, Hongo K: Ruptured distal middle cerebral artery aneurysm. J Neurosurg 100: 384– 388, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Horiuchi T, Tanaka Y, Hongo K, Nitta J, Kusano Y, Kobayashi S: Characteristics of distal posteroinferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 53: 589– 595; discussion 595–596, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Joo SP, Kim TS, Choi JW, Lee JK, Kim YS, Moon KS, Kim JH, Kim SH: Characteristics and management of ruptured distal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149: 661–667, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

