Genetically engineered pigs and target-specific immunomodulation provide significant graft survival and hope for clinical cardiac xenotransplantation
- PMID: 24998698
- PMCID: PMC4135017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.06.002
Genetically engineered pigs and target-specific immunomodulation provide significant graft survival and hope for clinical cardiac xenotransplantation
Abstract
Objectives: Cardiac transplantation and available mechanical alternatives are the only possible solutions for end-stage cardiac disease. Unfortunately, because of the limited supply of human organs, xenotransplantation may be the ideal method to overcome this shortage. We have recently seen significant prolongation of heterotopic cardiac xenograft survival from 3 to 12 months and beyond.
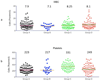
Methods: Hearts from genetically engineered piglets that were alpha 1-3 galactosidase transferase knockout and expressed the human complement regulatory gene, CD46 (groups A-C), and the human thrombomodulin gene (group D) were heterotropically transplanted in baboons treated with antithymocyte globulin, cobra venom factor, anti-CD20 antibody, and costimulation blockade (anti-CD154 antibody [clone 5C8]) in group A, anti-CD40 antibody (clone 3A8; 20 mg/kg) in group B, clone 2C10R4 (25 mg/kg) in group C, or clone 2C10R4 (50 mg/kg) in group D, along with conventional nonspecific immunosuppressive agents.
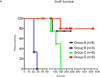
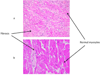
Results: Group A grafts (n = 8) survived for an average of 70 days, with the longest survival of 236 days. Some animals in this group (n = 3) developed microvascular thrombosis due to platelet activation and consumption, which resulted in spontaneous hemorrhage. The median survival time was 21 days in group B (n = 3), 80 days in group C (n = 6), and more than 200 days in group D (n = 5). Three grafts in group D are still contracting well, with the longest ongoing graft survival surpassing the 1-year mark.
Conclusions: Genetically engineered pig hearts (GTKOhTg.hCD46.hTBM) with modified targeted immunosuppression (anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody) achieved long-term cardiac xenograft survival. This potentially paves the way for clinical xenotransplantation if similar survival can be reproduced in an orthotopic transplantation model.
Copyright © 2014 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Allen SJ, Sidebotham D. Postoperative care and complications after ventricular assist device implantation. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2012 Jun;26(2):231–246. - PubMed
-
- Mohiuddin MM, Singh AK, Corcoran PC, Hoyt RF, Thomas ML, 3rd, Lewis BG, et al. One-year heterotopic cardiac xenograft survival in a pig to baboon model. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2014 Feb;14(2):488–489. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

