Evaluation of Aroclor 1260 exposure in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 24998970
- PMCID: PMC4225625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.06.019
Evaluation of Aroclor 1260 exposure in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
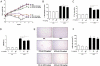
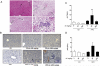
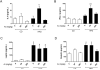
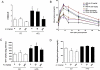
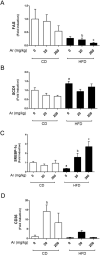
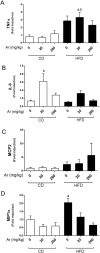
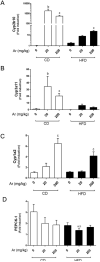
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent organic pollutants associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in epidemiologic studies. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the hepatic effects of a PCB mixture, Aroclor 1260, whose composition mimics human bioaccumulation patterns, in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity (DIO). Male C57Bl/6J mice were fed control diet or 42% high fat diet (HFD) and exposed to Aroclor 1260 (20mg/kg or 200mg/kg in corn oil) for 12weeks. A glucose tolerance test was performed; plasma/tissues were obtained at necropsy for measurements of adipocytokine levels, histology, and gene expression. Aroclor 1260 exposure was associated with decreased body fat in HFD-fed mice but had no effect on blood glucose/lipid levels. Paradoxically, Aroclor 1260+HFD co-exposed mice demonstrated increased hepatic inflammatory foci at both doses while the degree of steatosis did not change. Serum cytokines, ALT levels and hepatic expression of IL-6 and TNFα were increased only at 20mg/kg, suggesting an inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production at the 200mg/kg exposure. Aroclor 1260 induced hepatic expression of cytochrome P450s including Cyp3a11 (Pregnane-Xenobiotic Receptor target) and Cyp2b10 (constitutive androstane receptor target) but Cyp2b10 inducibility was diminished with HFD-feeding. Cyp1a2 (aryl hydrocarbon Receptor target) was induced only at 200mg/kg. In summary, Aroclor 1260 worsened hepatic and systemic inflammation in DIO. The results indicated a bimodal response of PCB-diet interactions in the context of inflammation which could potentially be explained by xenobiotic receptor activation. Thus, PCB exposure may be a relevant "second hit" in the transformation of steatosis to steatohepatitis.
Keywords: AhR; Aroclor 1260; CAR; NAFLD; PCBs; PXR.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Salman F, Plant N. Non-coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are direct agonists for the human pregnane-X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor, and activate target gene expression in a tissue-specific manner. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012;263:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Beyer A, Biziuk M. Environmental fate and global distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009;201:137–158. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Breivik K, Sweetman A, Pacyna JM, Jones KC. Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners—a mass balance approach. 1. Global production and consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2002;290:181–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

