MicroRNA Regulation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathogenesis
- PMID: 24999310
- PMCID: PMC4079820
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2014.14.3.138
MicroRNA Regulation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathogenesis
Abstract
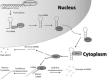
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small RNA molecules best known for their function in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Immunologically, miRNA regulates the differentiation and function of immune cells and its malfunction contributes to the development of various autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Over the last decade, accumulating researches provide evidence for the connection between dysregulated miRNA network and autoimmunity. Interruption of miRNA biogenesis machinery contributes to the abnormal T and B cell development and particularly a reduced suppressive function of regulatory T cells, leading to systemic autoimmune diseases. Additionally, multiple factors under autoimmune conditions interfere with miRNA generation via key miRNA processing enzymes, thus further skewing the miRNA expression profile. Indeed, several independent miRNA profiling studies reported significant differences between SLE patients and healthy controls. Despite the lack of a consistent expression pattern on individual dysregulated miRNAs in SLE among these studies, the aberrant expression of distinct groups of miRNAs causes overlapping functional outcomes including perturbed type I interferon signalling cascade, DNA hypomethylation and hyperactivation of T and B cells. The impact of specific miRNA-mediated regulation on function of major immune cells in lupus is also discussed. Although research on the clinical application of miRNAs is still immature, through an integrated approach with advances in next generation sequencing, novel tools in bioinformatics database analysis and new in vitro and in vivo models for functional evaluation, the diagnostic and therapeutic potentials of miRNAs may bring to fruition in the future.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; MicroRNAs; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:126–139. - PubMed
-
- Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:252–263. - PubMed
-
- Chen CZ, Li I, Lodish HF, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science. 2004;303:83–86. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

