Ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm: diagnosis and management
- PMID: 25000868
- PMCID: PMC4087178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.optom.2013.08.002
Ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm: diagnosis and management
Abstract
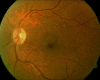
Retinal arterial macroaneurysm is an acquired, focal dilation of a retinal artery, typically occurring within the first three bifurcations of the central retinal artery. The clinical presentation of a retinal arterial macroaneurysm is highly variable, making initial diagnosis difficult and differentials many. Identification of retinal arterial macroaneurysms is crucial to appropriately co-manage with the primary care physician for hypertension control. Prognosis is generally good and observation is often an adequate treatment. However, in cases of macular threat or involvement, some treatment options are available and referral to a retinal specialist is indicated.
El macroaneurisma de la arteria retiniana es una dilatación focal y adquirida de una arteria retiniana, que se produce normalmente en de las primeras tres bifurcaciones de la arteria central de la retina. La presentación clínica del macroaneurisma de la arteria retiniana es altamente variable, lo que dificulta el diagnóstico inicial dadas las muchas características diferenciales. La identificación de dichos macroaneurismas es esencial para poder coordinar con el facultativo de atención primaria el control de la hipertensión. El pronóstico es generalmente bueno, siendo a menudo la observación el tratamiento adecuado. Sin embargo, en casos de amenaza o afectación macular, las opciones de tratamiento son variables, recomendándose la derivación al especialista de la retina.
Keywords: Exudación, hipertensión; Exudation; Hemorragia retiniana; Hypertension; Macroaneurisma de la arteria retiniana; Pérdida súbita de visión; Retinal arterial macroaneurysm; Retinal hemorrhage; Sudden vision loss.
Copyright © 2013 Spanish General Council of Optometry. Published by Elsevier Espana. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Rabb M., Gagliano D., Teske M. Retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Surv Ophthalmol. 1988;33:73–96. - PubMed
-
- Robertson D.M. Macroaneurysms of the retinal arteries. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1973;77:OP 55–OP 67. - PubMed
-
- Adamczyk A.T., Olivares G.E., Petito G.T. Retinal arterial macroaneurysm: a longitudinal case study. J Am Optom Assoc. 1989;60:840–845. - PubMed
-
- Holdeman N.R., Le H. Retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Clin Sur Ophthalmol. 2010;28(10/11):238–242.
-
- Bopp S. Retinal arterial macroaneurysms. In: Joussen A.M., Gardner T.W., Kirchhof B., Ryan SJ, editors. Retinal Vascular Disease [Internet] Springer-Verlag; New York, NY: 2007. pp. 543–560. Available from: http://www.springerlink.com/content/xh4171/#section=345175&page=3&locus=41 [accessed 28.2.11]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

