Mechanical signaling in reproductive tissues: mechanisms and importance
- PMID: 25001021
- PMCID: PMC4212346
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719114542023
Mechanical signaling in reproductive tissues: mechanisms and importance
Abstract
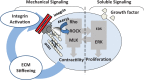
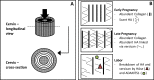
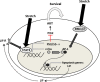
The organs of the female reproductive system are among the most dynamic tissues in the human body, undergoing repeated cycles of growth and involution from puberty through menopause. To achieve such impressive plasticity, reproductive tissues must respond not only to soluble signals (hormones, growth factors, and cytokines) but also to physical cues (mechanical forces and osmotic stress) as well. Here, we review the mechanisms underlying the process of mechanotransduction-how signals are conveyed from the extracellular matrix that surrounds the cells of reproductive tissues to the downstream molecules and signaling pathways that coordinate the cellular adaptive response to external forces. Our objective was to examine how mechanical forces contribute significantly to physiological functions and pathogenesis in reproductive tissues. We highlight how widespread diseases of the reproductive tract, from preterm labor to tumors of the uterus and breast, result from an impairment in mechanical signaling.
Keywords: ROCK/Rho kinase; cervical insufficiency; endometriosis; extracellular matrix; fibroids; mechanotransduction.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bissel MJ, Hall HG, Parry G. How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J Theor Biol. 1982;99 (1):31–68 - PubMed
-
- Ingber DE. Integrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991;3 (5):841–848 - PubMed
-
- Ingber DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. FASEB J. 2006;20 (7):811–827 - PubMed
-
- Sukharev S, Corey D. Mechanosensitive channels: multiplicity of families and gating paradigms. Sci STKE. 2004;2004(219):re4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

