A hydrophobic barrier deep within the inner pore of the TWIK-1 K2P potassium channel
- PMID: 25001086
- PMCID: PMC4102122
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5377
A hydrophobic barrier deep within the inner pore of the TWIK-1 K2P potassium channel
Abstract
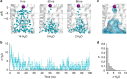
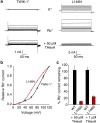
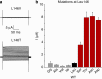
Recent X-ray crystal structures of the two-pore domain (K2P) family of potassium channels have revealed a unique structural architecture at the point where the cytoplasmic bundle-crossing gate is found in most other tetrameric K(+) channels. However, despite the apparently open nature of the inner pore in the TWIK-1 (K2P1/KCNK1) crystal structure, the reasons underlying its low levels of functional activity remain unclear. In this study, we use a combination of molecular dynamics simulations and functional validation to demonstrate that TWIK-1 possesses a hydrophobic barrier deep within the inner pore, and that stochastic dewetting of this hydrophobic constriction acts as a major barrier to ion conduction. These results not only provide an important insight into the mechanisms which control TWIK-1 channel activity, but also have important implications for our understanding of how ion permeation may be controlled in similar ion channels and pores.
Figures





References
-
- Enyedi P. & Czirjak G. Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol. Rev. 90, 559–605 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Mathie A. & Veale E. L. Therapeutic potential of neuronal two-pore domain potassium-channel modulators. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 8, 555–562 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Es-Salah-Lamoureux Z., Steele D. F. & Fedida D. Research into the therapeutic roles of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 31, 587–595 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Zhang X. & Chen H. TWIK-1 two-pore domain potassium channels change ion selectivity and conduct inward leak sodium currents in hypokalemia. Sci. Signal. 4, ra37 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/L002558/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/B/16011/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BEP17032/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- B19456/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H000267/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

