Cryoelectron microscopic structures of eukaryotic translation termination complexes containing eRF1-eRF3 or eRF1-ABCE1
- PMID: 25001285
- PMCID: PMC6813808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.058
Cryoelectron microscopic structures of eukaryotic translation termination complexes containing eRF1-eRF3 or eRF1-ABCE1
Abstract
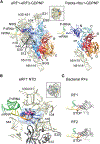
Termination and ribosome recycling are essential processes in translation. In eukaryotes, a stop codon in the ribosomal A site is decoded by a ternary complex consisting of release factors eRF1 and guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound eRF3. After GTP hydrolysis, eRF3 dissociates, and ABCE1 can bind to eRF1-loaded ribosomes to stimulate peptide release and ribosomal subunit dissociation. Here, we present cryoelectron microscopic (cryo-EM) structures of a pretermination complex containing eRF1-eRF3 and a termination/prerecycling complex containing eRF1-ABCE1. eRF1 undergoes drastic conformational changes: its central domain harboring the catalytically important GGQ loop is either packed against eRF3 or swung toward the peptidyl transferase center when bound to ABCE1. Additionally, in complex with eRF3, the N-terminal domain of eRF1 positions the conserved NIKS motif proximal to the stop codon, supporting its suggested role in decoding, yet it appears to be delocalized in the presence of ABCE1. These results suggest that stop codon decoding and peptide release can be uncoupled during termination.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
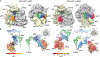

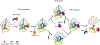
Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structure of the mammalian eukaryotic release factor eRF1-eRF3-associated termination complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 6;109(45):18413-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216730109. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23091004 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal interaction of translational release factors eRF1 and eRF3 of fission yeast: G-domain uncoupled binding and the role of conserved amino acids.RNA. 1999 Jun;5(6):739-50. doi: 10.1017/s135583829998216x. RNA. 1999. PMID: 10376874 Free PMC article.
-
Translation termination depends on the sequential ribosomal entry of eRF1 and eRF3.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 21;47(9):4798-4813. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz177. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30873535 Free PMC article.
-
Structural view on recycling of archaeal and eukaryotic ribosomes after canonical termination and ribosome rescue.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Dec;22(6):786-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 23031510 Review.
-
Translation Termination and Ribosome Recycling in Eukaryotes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Oct 1;10(10):a032656. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032656. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 29735640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Nonsense Mutations by New Emerging Technologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 20;21(12):4394. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124394. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32575694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hidden intrinsic ability of bicistronic expression based on a novel translation reinitiation mechanism in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Mar 20;53(6):gkaf220. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf220. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40156854 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):65-107. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186221. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27183566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PABP enhances release factor recruitment and stop codon recognition during translation termination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 19;44(16):7766-76. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw635. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27418677 Free PMC article.
-
The Structural Dynamics of Translation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2022 Jun 21;91:245-267. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-071921-122857. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Annu Rev Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35287473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkalaeva EZ, Pisarev AV, Frolova LY, Kisselev LL, and Pestova TV. (2006). In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell 125, 1125–1136. - PubMed
-
- Berninghausen O, and Beckmann R. (2011). Structure of the no-go mRNA decay complex Dom34-Hbs1 bound to a stalled 80S ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 18, 715–720. - PubMed
-
- Bhushan S, Meyer H, Starosta AL, Becker T, Mielke T, Berninghausen O, Sattler M, Wilson DN, and Beckmann R. (2010). Structural basis for translational stalling by human cytomegalovirus and fungal arginine attenuator peptide. Mol. Cell 40, 138–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

