Regulation of EGFR nanocluster formation by ionic protein-lipid interaction
- PMID: 25001389
- PMCID: PMC4123299
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2014.89
Regulation of EGFR nanocluster formation by ionic protein-lipid interaction
Abstract
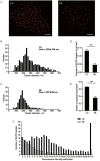
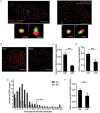
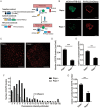
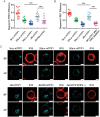
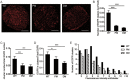
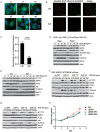
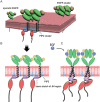
The abnormal activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is strongly associated with a variety of human cancers but the underlying molecular mechanism is not fully understood. By using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM), we find that EGFR proteins form nanoclusters in the cell membrane of both normal lung epithelial cells and lung cancer cells, but the number and size of clusters significantly increase in lung cancer cells. The formation of EGFR clusters is mediated by the ionic interaction between the anionic lipid phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) in the plasma membrane and the juxtamembrane (JM) region of EGFR. Disruption of EGFR clustering by PIP2 depletion or JM region mutation impairs EGFR activation and downstream signaling. Furthermore, JM region mutation in constitutively active EGFR mutant attenuates its capability of cell transformation. Collectively, our findings highlight the key roles of anionic phospholipids in EGFR signaling and function, and reveal a novel mechanism to explain the aberrant activation of EGFR in cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactions of the EGFR juxtamembrane domain with PIP2-containing lipid bilayers: Insights from multiscale molecular dynamics simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1850(5):1017-1025. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25219456 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants for membrane binding of the EGFR juxtamembrane domain.FEBS Lett. 2024 Jun;598(11):1402-1410. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14868. Epub 2024 Apr 8. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38589226
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor juxtamembrane region regulates allosteric tyrosine kinase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 4;104(49):19238-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703854104. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18042729 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-triggered resistance to molecular targeted drugs in lung cancer: roles of hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor ligands.Cancer Sci. 2012 Jul;103(7):1189-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02279.x. Epub 2012 May 9. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22435662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of EREG/EGFR Pathway in Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 27;22(23):12828. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312828. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A perspective of fluorescence microscopy for cellular structural biology with EGFR as witness.J Microsc. 2023 Jul;291(1):73-91. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13151. Epub 2022 Nov 4. J Microsc. 2023. PMID: 36282005 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface sculpting using logic-gated protein actuators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 18:2023.12.18.572113. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.18.572113. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38187604 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Fluorescence Imaging of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;14(3):686. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030686. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGFR oligomerization organizes kinase-active dimers into competent signalling platforms.Nat Commun. 2016 Oct 31;7:13307. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13307. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27796308 Free PMC article.
-
Lattice complex assembled by noncompetitive anti-EGFR antibodies regulates actin cytoskeletal reorganization.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Apr 21;20:129. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01204-z. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32336949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–354. - PubMed
-
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell. 2002;110:669–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

