Complexity of the 5'UTR region of the CLCN5 gene: eleven 5'UTR ends are differentially expressed in the human kidney
- PMID: 25001568
- PMCID: PMC4105828
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-41
Complexity of the 5'UTR region of the CLCN5 gene: eleven 5'UTR ends are differentially expressed in the human kidney
Abstract
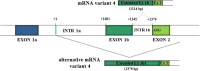
Background: Dent disease 1 represents a hereditary disorder of renal tubular epithelial function associated with mutations in the CLCN5 gene that encoded the ClC-5 Cl-/H+ antiporter. All of the reported disease-causing mutations are localized in the coding region except for one recently identified in the 5'UTR region of a single patient. This finding highlighted the possible role for genetic variability in this region in the pathogenesis of Dent disease 1.The structural complexity of the CLCN5 5'UTR region has not yet been fully characterized. To date 6 different 5' alternatively used exons--1a, 1b, 1b1 and I-IV with an alternatively spliced exon II (IIa, IIb)--have been described, but their significance and differential expression in the human kidney have not been investigated. Therefore our aim was to better characterize the CLCN5 5'UTR region in the human kidney and other tissues.
Methods: To clone more of the 5' end portion of the human CLCN5 cDNA, total human kidney RNA was utilized as template and RNA ligase-mediated rapid amplification of cDNA 5' ends was applied.The expression of the different CLCN5 isoforms was studied in the kidney, leucocytes and in different tissues by quantitative comparative RT/PCR and Real--Time RT/PCR.
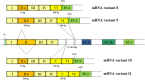
Results: Eleven transcripts initiating at 3 different nucleotide positions having 3 distinct promoters of varying strength were identified. Previously identified 5'UTR isoforms were confirmed, but their ends were extended. Six additional 5'UTR ends characterized by the presence of new untranslated exons (c, V and VI) were also identified. Exon c originates exon c.1 by alternative splicing. The kidney uniquely expresses all isoforms, and the isoform containing exon c appears kidney specific. The most abundant isoforms contain exon 1a, exon IIa and exons 1b1 and c. ORF analysis predicts that all isoforms except 3 encode for the canonical 746 amino acid ClC-5 protein.
Conclusions: Our results confirm the structural complexity of the CLCN5 5'UTR region. Characterization of this crucial region could allow a clear genetic classification of a greater number of Dent disease patients, but also provide the basis for highlighting some as yet unexplored functions of the ClC-5 proton exchanger.
Figures



Similar articles
-
From protein uptake to Dent disease: An overview of the CLCN5 gene.Gene. 2020 Jul 15;747:144662. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144662. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32289351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CLCN5 5'UTR isoforms in human kidneys: differential expression analysis between controls and patients with glomerulonephritis.J Investig Med. 2020 Apr;68(4):864-869. doi: 10.1136/jim-2019-001205. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Investig Med. 2020. PMID: 32019767 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel splice site mutation of CLCN5 gene and characterization of a new alternative 5' UTR end of ClC-5 mRNA in human renal tissue and leukocytes.J Hum Genet. 2004;49(1):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s10038-003-0108-1. Epub 2003 Dec 13. J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 14673707
-
A missense mutation in the chloride/proton ClC-5 antiporter gene results in increased expression of an alternative mRNA form that lacks exons 10 and 11. Identification of seven new CLCN5 mutations in patients with Dent's disease.J Hum Genet. 2007;52(3):255-261. doi: 10.1007/s10038-007-0112-y. Epub 2007 Jan 30. J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17262170
-
The Functional Meaning of 5'UTR in Protein-Coding Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):2976. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032976. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From protein uptake to Dent disease: An overview of the CLCN5 gene.Gene. 2020 Jul 15;747:144662. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144662. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32289351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Transcriptional Repressor Gene MSX1 Variations for Possible Associations with Congenital Heart Diseases.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142666. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26556783 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Analysis of the Renal Protective Effect of GLP-1 on Diabetic Patients Based on Edge Detection.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 22;2022:6504006. doi: 10.1155/2022/6504006. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35360475 Free PMC article.
-
Rs2459976 in ZW10 gene associated with congenital heart diseases in Chinese Han population.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 13;9(3):3867-3874. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23240. eCollection 2018 Jan 9. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29423089 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and phenotypic heterogeneity of Dent disease: the dark side of the moon.Hum Genet. 2021 Mar;140(3):401-421. doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02219-2. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 32860533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lloyd SE, Pearce SH, Fisher SE, Steinmeyer K, Schwappach B, Scheinman SJ, Harding B, Bolino A, Devoto M, Goodyer P, Rigden SP, Wrong O, Jentsch TJ, Craig IW, Thakker RV. A common molecular basis for three inherited kidney stone diseases. Nature. 1996;7(6564):445–449. - PubMed
-
- Hayama A, Uchida S, Sasaki S, Marumo F. Isolation and characterization of the human CLC-5 chloride channel gene promoter. Gene. 2000;7:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Fisher SE, Van Bakel I, Lloyd SE, Pearce SHS, Thakker RV, Craig IW. Cloning and characterization of CLCN5, the human kidney chloride channel gene implicated in Dent disease (an X-linked hereditary nephrolithiasis) Genomics. 1995;7(3):598–606. - PubMed
-
- Forino M, Graziotto R, Tosetto E, Gambaro G, D’Angelo A, Anglani F. Identification of a novel splice site mutation of CLCN5 gene and characterization of a new alternative 5′ UTR end of ClC-5 mRNA in human renal tissue and leukocytes. J Hum Genet. 2004;7(1):53–60. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig M, Waldegger S, Nuutinen M, Bökenkamp A, Reissinger A, Steckelbroeck S, Utsch B. Four additional CLCN5 exons encode a widely expressed novel long ClC-5 isoform but fail to explain Dent’s phenotype in patients without mutations in the short variant. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2003;7(3):176–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

