Severe Acinetobacter baumannii sepsis is associated with elevation of pentraxin 3
- PMID: 25001601
- PMCID: PMC4187799
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01958-14
Severe Acinetobacter baumannii sepsis is associated with elevation of pentraxin 3
Abstract
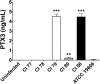
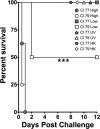
Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii is among the most prevalent bacterial pathogens associated with trauma-related wound and bloodstream infections. Although septic shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation have been reported following fulminant A. baumannii sepsis, little is known about the protective host immune response to this pathogen. In this study, we examined the role of PTX3, a soluble pattern recognition receptor with reported antimicrobial properties and stored within neutrophil granules. PTX3 production by murine J774a.1 macrophages was assessed following challenge with A. baumannii strains ATCC 19606 and clinical isolates (CI) 77, 78, 79, 80, and 86. Interestingly, only CI strains 79, 80, and 86 induced PTX3 synthesis in murine J774a.1 macrophages, with greatest production observed following CI 79 and 86 challenge. Subsequently, C57BL/6 mice were challenged intraperitoneally with CI 77 and 79 to assess the role of PTX3 in vivo. A. baumannii strain CI 79 exhibited significantly (P < 0.0005) increased mortality, with an approximate 50% lethal dose (LD50) of 10(5) CFU, while an equivalent dose of CI 77 exhibited no mortality. Plasma leukocyte chemokines (KC, MCP-1, and RANTES) and myeloperoxidase activity were also significantly elevated following challenge with CI 79, indicating neutrophil recruitment/activation associated with significant elevation in serum PTX3 levels. Furthermore, 10-fold-greater PTX3 levels were observed in mouse serum 12 h postchallenge, comparing CI 79 to CI 77 (1,561 ng/ml versus 145 ng/ml), with concomitant severe pathology (liver and spleen) and coagulopathy. Together, these results suggest that elevation of PTX3 is associated with fulminant disease during A. baumannii sepsis.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vaccination with a live attenuated Acinetobacter baumannii deficient in thioredoxin provides protection against systemic Acinetobacter infection.Vaccine. 2017 Jun 8;35(26):3387-3394. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 May 15. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28522011 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune responses to systemic Acinetobacter baumannii infection in mice: neutrophils, but not interleukin-17, mediate host resistance.Infect Immun. 2011 Aug;79(8):3317-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00069-11. Epub 2011 May 16. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21576323 Free PMC article.
-
Source of Circulating Pentraxin 3 in Septic Shock Patients.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3048. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03048. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30687307 Free PMC article.
-
Tug of war between Acinetobacter baumannii and host immune responses.Pathog Dis. 2018 Dec 1;76(9):ftz004. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftz004. Pathog Dis. 2018. PMID: 30657912 Review.
-
Mucosal immunization with purified OmpA elicited protective immunity against infections caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Microb Pathog. 2016 Jul;96:20-5. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Microb Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27133268 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Evaluation of an Immunoinformatics-Based Multi-Peptide Vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;12(4):358. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040358. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675740 Free PMC article.
-
Acute intraperitoneal infection with a hypervirulent Acinetobacter baumannii isolate in mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 25;9(1):6538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43000-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31024025 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with a live attenuated Acinetobacter baumannii deficient in thioredoxin provides protection against systemic Acinetobacter infection.Vaccine. 2017 Jun 8;35(26):3387-3394. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 May 15. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28522011 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin Modulates Cell Surface Hydrophobicity in Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 11;10:2849. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02849. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921031 Free PMC article.
-
Using an Aluminum Hydroxide-Chitosan Matrix Increased the Vaccine Potential and Immune Response of Mice against Multi-Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;11(3):669. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030669. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scott P, Petersen K, Fishbain J, Craft D, Ewell A, Moran K, Hack D, Deye G, Riddell S, Christopher G, Mancuso J, Petruccelli B, Endy T, Lindler L, Davis K, Milstrey E, Brosch L, Pool J, Blankenship C, Witt C, Malone J, Tornberg D, Srinivasan A. 2004. Acinetobacter baumannii infections among patients at military medical facilities treating injured U.S. service members, 2002–2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 53:1063–1066 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

