Bacterial type III secretion systems: specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells
- PMID: 25002086
- PMCID: PMC4388319
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155725
Bacterial type III secretion systems: specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells
Abstract
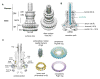
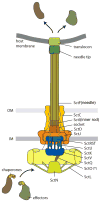
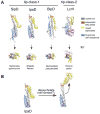
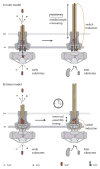
One of the most exciting developments in the field of bacterial pathogenesis in recent years is the discovery that many pathogens utilize complex nanomachines to deliver bacterially encoded effector proteins into target eukaryotic cells. These effector proteins modulate a variety of cellular functions for the pathogen's benefit. One of these protein-delivery machines is the type III secretion system (T3SS). T3SSs are widespread in nature and are encoded not only by bacteria pathogenic to vertebrates or plants but also by bacteria that are symbiotic to plants or insects. A central component of T3SSs is the needle complex, a supramolecular structure that mediates the passage of the secreted proteins across the bacterial envelope. Working in conjunction with several cytoplasmic components, the needle complex engages specific substrates in sequential order, moves them across the bacterial envelope, and ultimately delivers them into eukaryotic cells. The central role of T3SSs in pathogenesis makes them great targets for novel antimicrobial strategies.
Keywords: bacterial pathogenesis; molecular machines; protein secretion.
Figures
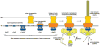
References
-
- Akeda Y, Galan JE. Chaperone release and unfolding of substrates in type III secretion. Nature. 2005;437:911–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

