Palmitoylation of plakophilin is required for desmosome assembly
- PMID: 25002405
- PMCID: PMC4150063
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.149849
Palmitoylation of plakophilin is required for desmosome assembly
Abstract
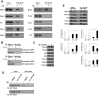
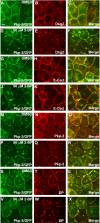
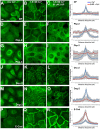
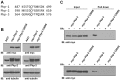
Desmosomes are prominent adhesive junctions found in various epithelial tissues. The cytoplasmic domains of desmosomal cadherins interact with a host of desmosomal plaque proteins, including plakophilins, plakoglobin and desmoplakin, which, in turn, recruit the intermediate filament cytoskeleton to sites of cell-cell contact. Although the individual components of the desmosome are known, mechanisms regulating the assembly of this junction are poorly understood. Protein palmitoylation is a posttranslational lipid modification that plays an important role in protein trafficking and function. Here, we demonstrate that multiple desmosomal components are palmitoylated in vivo. Pharmacologic inhibition of palmitoylation disrupts desmosome assembly at cell-cell borders. We mapped the site of plakophilin palmitoylation to a conserved cysteine residue present in the armadillo repeat domain. Mutation of this single cysteine residue prevents palmitoylation, disrupts plakophilin incorporation into the desmosomal plaque and prevents plakophilin-dependent desmosome assembly. Finally, plakophilin mutants unable to become palmitoylated act in a dominant-negative manner to disrupt proper localization of endogenous desmosome components and decrease desmosomal adhesion. Taken together, these data demonstrate that palmitoylation of desmosomal components is important for desmosome assembly and adhesion.
Keywords: Desmosome; Palmitoylation; Plakophilin.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
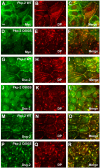
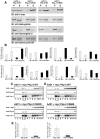
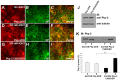
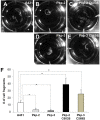
Similar articles
-
Plakophilin 1 interferes with plakoglobin binding to desmoplakin, yet together with plakoglobin promotes clustering of desmosomal plaque complexes at cell-cell borders.J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 4):727-38. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.4.727. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11171378
-
The head domain of plakophilin-1 binds to desmoplakin and enhances its recruitment to desmosomes. Implications for cutaneous disease.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 25;274(26):18145-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.26.18145. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10373410
-
The desmosome.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Aug;1(2):a002543. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002543. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20066089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plakoglobin is required for effective intermediate filament anchorage to desmosomes.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Nov;128(11):2665-2675. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.141. Epub 2008 May 22. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18496566
-
Regulation of desmosome assembly and adhesion.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Dec;15(6):665-77. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2004.09.005. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15561586 Review.
Cited by
-
Desmosomal Cadherins in Health and Disease.Annu Rev Pathol. 2022 Jan 24;17:47-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-042320-092912. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Annu Rev Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34425055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
zDHHC-Mediated S-Palmitoylation in Skin Health and Its Targeting as a Treatment Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 15;26(4):1673. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041673. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global identification of S-palmitoylated proteins and detection of palmitoylating (DHHC) enzymes in heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Jun;155:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.02.007. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33636221 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA- and cytokine-associated extracellular vesicles mediate squamous cell carcinomas.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jul 13;9(1):1790159. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1790159. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32944178 Free PMC article.
-
The desmosome is a mesoscale lipid raft-like membrane domain.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Jun 1;30(12):1390-1405. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-10-0649. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30943110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazzi H., Getz A., Mahoney M. G., Ishida-Yamamoto A., Langbein L., Wahl J. K., 3rd, Christiano A. M. (2006). Desmoglein 4 is expressed in highly differentiated keratinocytes and trichocytes in human epidermis and hair follicle. Differentiation 74, 129–140 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2006.00061.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

