Chitin accelerates activation of a novel haloarchaeal serine protease that deproteinizes chitin-containing biomass
- PMID: 25002433
- PMCID: PMC4178621
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01196-14
Chitin accelerates activation of a novel haloarchaeal serine protease that deproteinizes chitin-containing biomass
Abstract
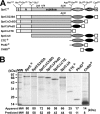
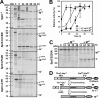
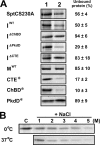
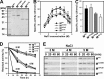
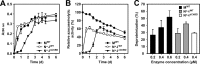
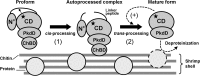
The haloarchaeon Natrinema sp. strain J7-2 has the ability to degrade chitin, and its genome harbors a chitin metabolism-related gene cluster that contains a halolysin gene, sptC. The sptC gene encodes a precursor composed of a signal peptide, an N-terminal propeptide consisting of a core domain (N*) and a linker peptide, a subtilisin-like catalytic domain, a polycystic kidney disease domain (PkdD), and a chitin-binding domain (ChBD). Here we report that the autocatalytic maturation of SptC is initiated by cis-processing of N* to yield an autoprocessed complex (N*-I(WT)), followed by trans-processing/degradation of the linker peptide, the ChBD, and N*. The resulting mature form (M(WT)) containing the catalytic domain and the PkdD showed optimum azocaseinolytic activity at 3 to 3.5 M NaCl, demonstrating salt-dependent stability. Deletion analysis revealed that the PkdD did not confer extra stability on the enzyme but did contribute to enzymatic activity. The ChBD exhibited salt-dependent chitin-binding capacity and mediated the binding of N*-I(WT) to chitin. ChBD-mediated chitin binding enhances SptC maturation by promoting activation of the autoprocessed complex. Our results also demonstrate that SptC is capable of removing proteins from shrimp shell powder (SSP) at high salt concentrations. Interestingly, N*-I(WT) released soluble peptides from SSP faster than did M(WT). Most likely, ChBD-mediated binding of the autoprocessed complex to chitin in SSP not only accelerates enzyme activation but also facilitates the deproteinization process by increasing the local protease concentration around the substrate. By virtue of these properties, SptC is highly attractive for use in preparation of chitin from chitin-containing biomass.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sec-Dependent Secretion of Subtilase SptE in Haloarchaea Facilitates Its Proper Folding and Heterocatalytic Processing by Halolysin SptA Extracellularly.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Apr 26;88(8):e0024622. doi: 10.1128/aem.00246-22. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35348390 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for auto- and hetero-catalytic maturation of a thermostable subtilase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. WF146.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 29;288(48):34826-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.498774. Epub 2013 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24145031 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and characterization of the chitin-binding domain of chitinase A1 from Bacillus circulans WL-12.J Bacteriol. 2000 Jun;182(11):3045-54. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.11.3045-3054.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10809681 Free PMC article.
-
Auto- and Hetero-Catalytic Processing of the N-Terminal Propeptide Promotes the C-Terminal Fibronectin Type III Domain-Mediated Dimerization of a Thermostable Vpr-like Protease.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Nov 8;88(21):e0150322. doi: 10.1128/aem.01503-22. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36250702 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel chitin-binding protease from Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 and its role in the chitinolytic system.J Bacteriol. 2002 Apr;184(7):1865-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1865-1872.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11889092 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel halolysin without C-terminal extension from an extremely halophilic archaeon.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Apr;106(8):3009-3019. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11903-4. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35435453
-
Recent advances in the production, properties and applications of haloextremozymes protease and lipase from haloarchaea.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 27;39(11):322. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03779-x. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37755613 Review.
-
A TrmBL2-like transcription factor mediates the growth phase-dependent expression of halolysin SptA in a concentration-dependent manner in Natrinema gari J7-2.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jul 24;90(7):e0074124. doi: 10.1128/aem.00741-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38953660 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Translation Initiation of a Haloarchaeal Serine Protease Transcript Containing Two In-Frame Start Codons.J Bacteriol. 2016 Jun 13;198(13):1892-901. doi: 10.1128/JB.00202-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27137502 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular proteases from halophiles: diversity and application challenges.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;107(19):5923-5934. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12721-y. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37566160 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

