Ras transformation uncouples the kinesin-coordinated cellular nutrient response
- PMID: 25002494
- PMCID: PMC4115560
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1411016111
Ras transformation uncouples the kinesin-coordinated cellular nutrient response
Abstract
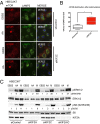
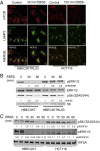
The kinesin family members (KIFs) KIF2A and KIF2C depolymerize microtubules, unlike the majority of other kinesins, which transport cargo along microtubules. KIF2A regulates the localization of lysosomes in the cytoplasm, which assists in activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) on the lysosomal surface. We find that the closely related kinesin KIF2C also influences lysosomal organization in immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs). Expression of KIF2C and, to a lesser extent, KIF2A in untransformed and mutant K-Ras-transformed cells is regulated by ERK1/2. Prolonged inhibition of ERK1/2 activation with PD0325901 mimics nutrient deprivation by disrupting lysosome organization and decreasing mTORC1 activity in HBEC, suggesting a long-term mechanism for optimization of mTORC1 activity by ERK1/2. We tested the hypothesis that up-regulation of KIF2C and KIF2A by ERK1/2 caused aberrant lysosomal positioning and mTORC1 activity in a mutant K-Ras-dependent cancer and cancer model. In Ras-transformed cells, however, mTORC1 activity and lysosome organization appear independent of ERK1/2 and these kinesins although ERK1/2 activity and the kinesins are required for Ras-dependent proliferation and migration. We conclude that mutant K-Ras repurposes these signaling and regulatory proteins to support the transformed phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ras regulates kinesin 13 family members to control cell migration pathways in transformed human bronchial epithelial cells.Oncogene. 2014 Nov 20;33(47):5457-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.486. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24240690 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 upregulation via ERK-dependent gene expression change confers intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibitors in oncogenic KRas-mutant cancer cells.Oncogene. 2015 Nov 5;34(45):5607-16. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.16. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25703330
-
S6K1 alternative splicing modulates its oncogenic activity and regulates mTORC1.Cell Rep. 2013 Jan 31;3(1):103-15. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.020. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23273915 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by amino acids.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;24(7):400-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24698685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acids and mTORC1: from lysosomes to disease.Trends Mol Med. 2012 Sep;18(9):524-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.05.007. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Trends Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22749019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KIF2A Overexpression and Its Association with Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Poor Prognoses in Patients with Gastric Cancer.Dis Markers. 2016;2016:7484516. doi: 10.1155/2016/7484516. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Dis Markers. 2016. PMID: 27773961 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circ_0010235 sponges miR-338-3p to play oncogenic role in proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through modulating KIF2A.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):693-706. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1925736. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34024242 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Biomarkers for Controlling Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics in Bladder Cancer by Network Analysis of Transcriptome Data Stemness Indices.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 4;9:613. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00613. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31334127 Free PMC article.
-
The Overexpression of Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A (KIF2A) was Associated with the Proliferation and Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 May 20;12:3731-3739. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S248008. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Mar 07;14:981-982. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S364909. PMID: 32547209 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Human Mitotic Centromere-Associated Kinesin Is Targeted by MicroRNA 485-5p/181c and Prognosticates Poor Survivability of Breast Cancer.J Oncol. 2019 Apr 3;2019:2316237. doi: 10.1155/2019/2316237. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31073307 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

