TRP14 inhibits osteoclast differentiation via its catalytic activity
- PMID: 25002534
- PMCID: PMC4135626
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00293-14
TRP14 inhibits osteoclast differentiation via its catalytic activity
Abstract
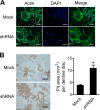
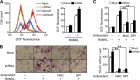
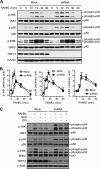
We previously reported the inhibitory role of thioredoxin-related protein of 14 kDa (TRP14), a novel disulfide reductase, in nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, but its biological function has remained to be explored. Here, we evaluated the role of TRP14 in the differentiation and function of osteoclasts (OCs), for which NF-κB and cellular redox regulation have been known to be crucial, using RAW 264.7 macrophage cells expressing wild-type TRP14 or a catalytically inactive mutant, as well as its small interfering RNA. TRP14 depletion enhanced OC differentiation, actin ring formation, and bone resorption, as well as the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). TRP14 depletion promoted the activation of NF-κB, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and p38, the expression of c-Fos, and the consequent induction of nuclear factor of activated T cell, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1), a key determinant of osteoclastogenesis. However, pretreatment with N-acetylcysteine or diphenylene iodonium significantly reduced the OC differentiation, as well as the ROS accumulation and NF-κB activation, that were enhanced by TRP14 depletion. Furthermore, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced ROS accumulation, NF-κB activation, and OC differentiation were inhibited by the ectopic expression of wild-type TRP14 but not by its catalytically inactive mutant. These results suggest that TRP14 regulates OC differentiation and bone resorption through its catalytic activity and that enhancing TRP14 may present a new strategy for preventing bone resorption diseases.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
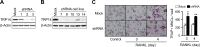


Similar articles
-
Nrf2 deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23954472
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Acteoside suppresses RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting c-Fos induction and NF-κB pathway and attenuating ROS production.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 4;8(12):e80873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080873. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24324641 Free PMC article.
-
Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Loss via Activating ROS-Dependent NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 23;14(19):3955. doi: 10.3390/nu14193955. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235607 Free PMC article.
-
Maslinic acid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by regulating RANKL-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26(3):644-56. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.242. J Bone Miner Res. 2011. PMID: 20814972
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-related protein of 14 kDa as a modulator of redox signalling pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;176(4):544-553. doi: 10.1111/bph.14479. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30129655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-Denitrosylation: A Crosstalk between Glutathione and Redoxin Systems.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;11(10):1921. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101921. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dehydrocostus lactone inhibits NFATc1 via regulation of IKK, JNK, and Nrf2, thereby attenuating osteoclastogenesis.BMB Rep. 2020 Apr;53(4):218-222. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2020.53.4.220. BMB Rep. 2020. PMID: 31964469 Free PMC article.
-
Unfractionated Heparin Promotes Osteoclast Formation in Vitro by Inhibiting Osteoprotegerin Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 22;17(4):613. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040613. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27110777 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Fermented Oyster Extract against RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis through Scavenging ROS Generation in RAW 264.7 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1439. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061439. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong BR, Rho J, Arron J, Robinson E, Orlinick J, Chao M, Kalachikov S, Cayani E, Bartlett FS, III, Frankel WN, Lee SY, Choi Y. 1997. TRANCE is a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272:25190–25194. 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25190 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Suda T. 1998. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95:3597–3602. 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3597 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
