Sirtuin1 (Sirt1) promotes cortical bone formation by preventing β-catenin sequestration by FoxO transcription factors in osteoblast progenitors
- PMID: 25002589
- PMCID: PMC4148840
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.561803
Sirtuin1 (Sirt1) promotes cortical bone formation by preventing β-catenin sequestration by FoxO transcription factors in osteoblast progenitors
Abstract
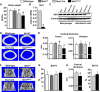
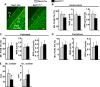
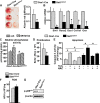
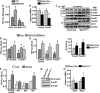
A decline of the levels and activity of Sirtuin1 (Sirt1), a NAD(+) class III histone deacetylase, with age contributes to the development of several diseases including type 2 diabetes, neurodegeneration, inflammation, and cancer. The anti-aging effects of Sirt1 evidently result from the deacetylation of many transcription factors and co-factors including members of the Forkhead box O (FoxO) family and β-catenin. Wnt/β-catenin is indispensable for osteoblast generation. FoxOs, on the other hand, sequester β-catenin and inhibit osteoprogenitor proliferation. Here, we have deleted Sirt1 in osteoprogenitors expressing Osterix1 (Osx1)-Cre and their descendants. Sirt1(ΔOsx1) mice had lower cortical thickness in femora and vertebrae because of reduced bone formation at the endocortical surface. In line with this, osteoprogenitor cell cultures from the Sirt1(ΔOsx1) mice exhibited lower alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization, as well as decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis. These changes were associated with decreased Wnt/β-catenin signaling and expression of cyclin D1 and resulted from increased binding of FoxOs to β-catenin. These findings demonstrate that Sirt1-induced deacetylation of FoxOs unleashes Wnt signaling. A decline in Sirt1 activity in osteoblast progenitors with aging may, therefore, contribute to the age-related loss of bone mass. Together with evidence that Sirt1 activators increase bone mass in aged mice, our results also suggest that Sirt1 could be a therapeutic target for osteoporosis.
Keywords: Animal Model; Apoptosis; Cell Proliferation; Osteoporosis; Wnt Signaling.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress antagonizes Wnt signaling in osteoblast precursors by diverting beta-catenin from T cell factor- to forkhead box O-mediated transcription.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 14;282(37):27298-27305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702811200. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17623658
-
A decrease in NAD+ contributes to the loss of osteoprogenitors and bone mass with aging.NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2021 Apr 1;7(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41514-021-00058-7. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2021. PMID: 33795658 Free PMC article.
-
FOXOs attenuate bone formation by suppressing Wnt signaling.J Clin Invest. 2013 Aug;123(8):3409-19. doi: 10.1172/JCI68049. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23867625 Free PMC article.
-
Gone with the Wnts: beta-catenin, T-cell factor, forkhead box O, and oxidative stress in age-dependent diseases of bone, lipid, and glucose metabolism.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Nov;21(11):2605-14. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0259. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17622581 Review.
-
The Role of FoxOs in Bone Health and Disease.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018;127:149-163. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2017.10.004. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29433736 Review.
Cited by
-
The Spectrum of Fundamental Basic Science Discoveries Contributing to Organismal Aging.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Sep;33(9):1568-1584. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3564. Epub 2018 Aug 13. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 30075061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by lithium chloride attenuates d-galactose-induced neurodegeneration in the auditory cortex of a rat model of aging.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Apr 25;7(6):759-776. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12220. eCollection 2017 Jun. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28593132 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO1 promotes the expression of canonical WNT target genes in examined basal-like breast and glioblastoma multiforme cancer cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Nov;13(11):2108-2123. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13696. Epub 2023 Aug 28. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37584250 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin and diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2015 Oct 25;6(14):1259-73. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i14.1259. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26516410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 is a positive regulator of the master osteoblast transcription factor, RUNX2.PLoS One. 2017 May 25;12(5):e0178520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178520. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manolagas S. C. (2000) Birth and death of bone cells: basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 21, 115–137 - PubMed
-
- Long F. (2012) Building strong bones: molecular regulation of the osteoblast lineage. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 27–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

