Rac1 and Aurora A regulate MCAK to polarize microtubule growth in migrating endothelial cells
- PMID: 25002679
- PMCID: PMC4085700
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201401063
Rac1 and Aurora A regulate MCAK to polarize microtubule growth in migrating endothelial cells
Abstract
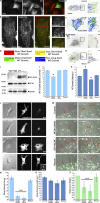
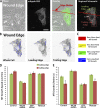
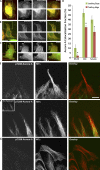
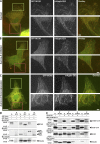
Endothelial cells (ECs) migrate directionally during angiogenesis and wound healing by polarizing to extracellular cues to guide directional movement. EC polarization is controlled by microtubule (MT) growth dynamics, which are regulated by MT-associated proteins (MAPs) that alter MT stability. Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK) is a MAP that promotes MT disassembly within the mitotic spindle, yet its function in regulating MT dynamics to promote EC polarity and migration has not been investigated. We used high-resolution fluorescence microscopy coupled with computational image analysis to elucidate the role of MCAK in regulating MT growth dynamics, morphology, and directional migration of ECs. Our results show that MCAK-mediated depolymerization of MTs is specifically targeted to the trailing edge of polarized wound-edge ECs. Regulation of MCAK function is dependent on Aurora A kinase, which is regionally enhanced by signaling from the small guanosine triphosphatase, Rac1. Thus, a Rac1-Aurora A-MCAK signaling pathway mediates EC polarization and directional migration by promoting regional differences in MT dynamics in the leading and trailing cell edges.
© 2014 Braun et al.
Figures

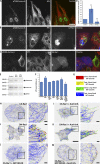
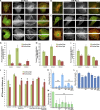
References
-
- Akhmanova, A., Hoogenraad C.C., Drabek K., Stepanova T., Dortland B., Verkerk T., Vermeulen W., Burgering B.M., De Zeeuw C.I., Grosveld F., and Galjart N.. 2001. Clasps are CLIP-115 and -170 associating proteins involved in the regional regulation of microtubule dynamics in motile fibroblasts. Cell. 104:923–935 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00288-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

