Unusual occurrence of supratentorial medulloepithelioma in a young female
- PMID: 25002766
- PMCID: PMC4078611
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-3147.133582
Unusual occurrence of supratentorial medulloepithelioma in a young female
Abstract
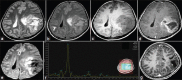
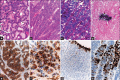
Medulloepithelioma is an extremely rare PNET in late adolescence and adults with only two cases noted in literature. These are WHO grade IV tumors with dismal prognosis. Only few cases survived beyond 5 months. We report a rare case of supratentorial medulloepithelioma in a 17 year old girl. She had presented with right sided weakness, headache and vomiting. Imaging showed an enhancing mass lesion in left parietal region which undergone gross total resection. After surgery, her headache, vomiting and right sided weakness improved. On histopathology, the tumor had characteristic trabecular, ribbon and palisaded arrangement with brisk mitotic activity, necrosis and calcification. Immuno-histochemistry revealed positivity for Synaptophysin, Vimentin and EMA while GFAP was negative. MIB-1 labeling was very high. Patient received postoperative radiotherapy. On follow up after 14 months, she was clinically asymptomatic with no recurrence on imaging.
Keywords: Late adolescence and adults; medulloepithelioma; primitive neuroectodermal tumor; supratentorial.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posterior cerebral fossa medulloepithelioma: report of a case.BMC Clin Pathol. 2017 Nov 21;17:23. doi: 10.1186/s12907-017-0064-x. eCollection 2017. BMC Clin Pathol. 2017. PMID: 29200961 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of a supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor using magnetic resonance-guided laser-induced thermal therapy.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2011 Nov;8(5):468-75. doi: 10.3171/2011.8.PEDS11148. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 22044371
-
[A supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor exhibiting pathological characteristics of medulloepithelioma: a case report].No Shinkei Geka. 2012 Feb;40(2):159-65. No Shinkei Geka. 2012. PMID: 22281469 Japanese.
-
Medulloepithelioma with heterologous osteoid component: a case report and review of literature.Childs Nerv Syst. 2019 Jun;35(6):1035-1039. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-04041-8. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Childs Nerv Syst. 2019. PMID: 30617578 Review.
-
Long-term survival in a child with a central nervous system medulloepithelioma.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008 Nov;2(5):339-45. doi: 10.3171/PED.2008.2.11.349. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008. PMID: 18976104 Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral ventricular medulloepithelioma in children: a case report.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):1020-1025. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-257. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moftakhar P, Fan X, Huevitz CH, Black KL, Danielpour M. Long-term survival in a child with a central nervous system medulloepithelioma. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008;2:339–45. - PubMed
-
- Lolova I, Bojinov S, Ivanova A, Christov V. Cerebral medulloepithelioma. Histological and histochemical study of a case. J Neurol Sci. 1972;15:173–82. - PubMed
-
- Caccamo DV, Herman MM, Rubinstein LJ. An immunohistochemical study of the primitive and maturing elements of human cerebral medulloepitheliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;79:248–54. - PubMed
-
- Gurney JG, Smith MA, Bunin GR. CNS and miscellaneous intracranial and intraspinal neoplasms. In: Reis LA, Smith MA, Gurney JG, Linet M, Tamra T, Young JL, et al., editors. Cancer incidence and survival among children and adolescents. Bethesda, MD: United States SEER program 1975-1995. National cancer institute SEER program, United States of America: NIH Publication; 1999. pp. 51–63. No. 99-4649.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
