Effects of siRNA targeting BMPR-II on the biological activities of human liver cancer cells and its mechanism
- PMID: 25002834
- PMCID: PMC4083141
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-14-55
Effects of siRNA targeting BMPR-II on the biological activities of human liver cancer cells and its mechanism
Abstract
Background: Bone morphogenetic protein receptor II (BMPR-II) plays an important role in tumor's invasion and proliferation. In this study, we observed the effects of small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting bone morphogenetic protein receptor II (BMPR-II) on the biological activities of human liver cells and explore its mechanism.
Methods: The molecular sequences of three siRNA targeting BMPR-IIwere designed and synthesized. In this study, there were 6 groups including group I (normal control), group II (blank control), group III (negative control) and group IV-VI (BMPR-II-siRNA-a, siRNA-b and siRNA-c-transfected cells, respectively). The levels of mRNA and protein of BMPR-II were determined to select the best sequence for BMPR-II silence. After liver cancer cells were transfected with the best sequence, proliferation and invasion of transfected cells were assessed, and apoptosis and cell cycle were detected. The expressions of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signal pathway-related VEGF-C protein were observed after BMPR-II silence and BMPR-II silence combined with inhibiting MAPKs signal pathway, respectively.
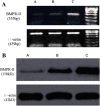
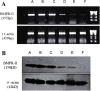
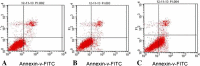
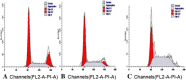
Results: RT-PCR and Western blot indicated that BMPR-II expression was the highest in HepG2 among the three liver cancer lines (P < 0.01) and the lowest in group IV among the six groups (P < 0.01). MTT assay and transwell assay revealed that the numbers of cell growth and cell transmembrane were significantly lower in group IV than in control groups 48 h after cells were transfected (P < 0.05). Flow cytometer showed that apoptosis was the highest and cells were significantly blocked in S phase 48 h after cells were transfected in group IV (P < 0.01). Western blot indicated that the protein levels of p-P38 (P < 0.01) and vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) (P < 0.01) were significantly decreased after BMPR-II silence. The protein level of VEGF-C was significantly decreased in PD98059 + siRNA-BMPR-II-a and SB203580 + siRNA-BMPR-II-a groups (P < 0.01), especially in SB203580 + siRNA-BMPR-II-a group (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: siRNA targeting BMPR-IIcan markedly inhibit HepG2 proliferation and invasion, promote apoptosis and block HepG2 in S phase. Its mechanism may be that BMPR-II silence down-regulates VEGF-C expression through MAPK/P38 and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways, especially MAPK/P38. This study provides a new targeted therapy for liver cancer.
Keywords: Bone morphogenetic protein receptor II; Liver cancer; Mitogen-activated protein kinases; Small interfering RNA; Vascular endothelial growth factor-C.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of siRNA-targeting BMP-2 on the abilities of migration and invasion of human liver cancer SMMC7721 cells and its mechanism.Cancer Gene Ther. 2011 Jan;18(1):20-5. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2010.55. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 20885449
-
[The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in inhibition of proliferation in human prostate carcinoma cells by raloxifene: an in vitro experiment].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Jan 22;88(4):271-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18361842 Chinese.
-
Effect of silencing NEK2 on biological behaviors of HepG2 in human hepatoma cells and MAPK signal pathway.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):2023-35. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3993-y. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26337275
-
Downregulation of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006 Mar;290(3):L450-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00206.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16361357
-
[Inhibitory effects of siRNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor on proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Sep 17;84(18):1503-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15500708 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in RNA Interference-Based Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Emphasis on siRNA.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1947-1964. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01395-6. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38987439 Review.
-
Prioritization of genes involved in endothelial cell apoptosis by their implication in lymphedema using an analysis of associative gene networks with ANDSystem.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Mar 13;12(Suppl 2):47. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0492-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30871556 Free PMC article.
-
Promotive effects of bone morphogenetic protein 2 on angiogenesis in hepatocarcinoma via multiple signal pathways.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 25;6:37499. doi: 10.1038/srep37499. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27886213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heinke J, Kerber M, Rahner S, Mnich L, Lassmann S, Helbing T, Heinke J, Kerber M, Rahner S, Mnich L, Lassmann S, Helbing T, Werner M, Patterson C, Bode C, Moser M. Bone morphogenetic protein modulator BMPER is highly expressed in malignant tumors and controls invasive cell behavior. Oncogene. 2012;31:2919–2930. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.473. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Song G, Li Y, Zhang Z, Ren X, Li H, Zhang W, Song G, Li Y, Zhang Z, Ren X, Li H, Zhang W, Wei R, Pan S, Shi L, Bi K, Jiang G. C-myc but not Hif-1α-dependent down-regulation of VEGF influences the proliferation and differentiation of HL-60 cells induced by ATRA. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:2378–2384. - PubMed
-
- Pi X, Schmitt CE, Xie L, Portbury AL, Wu Y, Lockyer P, Pi X, Schmitt CE, Xie L, Portbury AL, Wu Y, Lockyer P, Dyer LA, Moser M, Bu G, Flynn EJ 3rd, Jin SW, Patterson C. LRP1-dependent endocytic mechanism governs the signaling output of the bmp system in endothelial cells and inangiogenesis. Circ Res. 2012;111:564–574. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.274597. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

