Deep mineral water accelerates recovery after dehydrating aerobic exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study
- PMID: 25002835
- PMCID: PMC4083353
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-11-34
Deep mineral water accelerates recovery after dehydrating aerobic exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study
Abstract
Background: The effect of deep mineral water (DMW) with moderate mineralization on the recovery of physical performance after prolonged dehydrating aerobic exercise in the heat was studied in nine healthy, physically active (VO2max = 45.8 ± 8.4 mL kg(-1) min(-1)) women aged 24.0 ± 3.7 years.
Methods: We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover human study to evaluate the effect of ingestion of natural mineral water extracted from a depth of 689 m on recovery from prolonged fatiguing aerobic running conducted at 30°C.
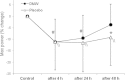
Results: Mean body weight decreased by 2.6-2.8% following dehydrating exercise. VO2max was 9% higher after 4 h of recovery after rehydrating with DMW compared with plain water. Leg muscle power recovered better during the slow phase of recovery and was significantly higher after 48 h of recovery after rehydrating with DMW compared with plain water.
Conclusions: DMW with moderate mineralization was more effective in inducing recovery of aerobic capacity and leg muscle power compared with plain water following prolonged dehydrating aerobic running exercise.
Keywords: Aerobic capacity; Deep mineral water; Leg muscle power; Recovery; Rehydration; Women.
Figures



References
-
- Maughan RJ, Shirreffs SM. Rehydration and recovery after exercise. A short survey. Sci Sports. 2004;19:2341–2348.
-
- Sawka MN, Montain SJ, Latzka WA. Hydration effects on thermoregulation and performance in the heat. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001;128:679–690. - PubMed
-
- Coyle EF. Fluid and fuel intake during exercise. J Sports Sci. 2004;22:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Mudambo KS, Leese GP, Rennie MJ. Dehydration in soldiers during walking/running exercise in the heat and the effects of fluid ingestion during and after exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1997;76:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Van den Eynde F, Van Baelen PC, Portzky M, Audenaert K. The effects of energy drinks on cognitive function. Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2008;50:273–281. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
