A multicenter approach evaluating the impact of vitamin e-blended polyethylene in cementless total hip replacement
- PMID: 25002933
- PMCID: PMC4083306
- DOI: 10.4081/or.2014.5285
A multicenter approach evaluating the impact of vitamin e-blended polyethylene in cementless total hip replacement
Abstract
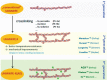
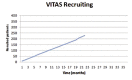
Since polyethylene is one of the most frequently used biomaterials as a liner in total hip arthroplasty, strong efforts have been made to improve design and material properties over the last 50 years. Antioxidants seems to be a promising alternative to further increase durability and reduce polyethylene wear in long term. As of yet, only in vitro results are available. While they are promising, there is yet no clinical evidence that the new material shows these advantages in vivo. To answer the question if vitamin-E enhanced ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is able to improve long-term survivorship of cementless total hip arthroplasty we initiated a randomized long-term multicenter trial. Designed as a superiority study, the oxidation index assessed in retrieval analyses of explanted liners was chosen as primary parameter. Radiographic results (wear rate, osteolysis, radiolucency) and functional outcome (Harris Hip Scores, University of California-Los Angeles, Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, Visual Analogue Scale) will serve as secondary parameters. Patients with the indication for a cementless total hip arthroplasty will be asked to participate in the study and will be randomized to either receive a standard hip replacement with a highly cross-linked UHMWPE-X liner or a highly cross-linked vitamin-E supplemented UHMWPE-XE liner. The follow-up will be 15 years, with evaluation after 5, 10 and 15 years. The controlled randomized study has been designed to determine if Vitamin-E supplemented highly cross-linked polyethylene liners are superior to standard XLPE liners in cementless total hip arthroplasty. While several studies have been started to evaluate the influence of vitamin-E, most of them evaluate wear rates and functional results. The approach used for this multicenter study, to analyze the oxidation status of retrieved implants, should make it possible to directly evaluate the ageing process and development of the implant material itself over a time period of 15 years.
Keywords: PE; UHMWPE; antioxidants; oxidation; randomized trial; total hip arthroplasty; vitamin-E; wear.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: based on written contracts with the participating study centers the VITAS™ study is financially supported by the sponsor (B. Braun-Aesculap AG, Tuttlingen, Germany).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cup positioning and its effect on polyethylene wear of vitamin E- and non-vitamin E-supplemented liners in total hip arthroplasty: radiographic outcome at 5-year follow-up.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Mar;143(3):1679-1688. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04424-2. Epub 2022 Apr 10. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 35397656 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vitamin E-blended highly cross-linked polyethylene liners in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, multicenter trial using virtual CAD-based wear analysis at 5-year follow-up.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020 Dec;140(12):1859-1866. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03358-x. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020. PMID: 32048017 Clinical Trial.
-
Vitamin E-blended versus conventional polyethylene liners in prostheses : Prospective, randomized trial with 3-year follow-up.Orthopade. 2020 Dec;49(12):1077-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00132-019-03830-6. Orthopade. 2020. PMID: 31696260 Clinical Trial. English.
-
Manufacturing, oxidation, mechanical properties and clinical performance of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty.Hip Int. 2018 Nov;28(6):573-583. doi: 10.1177/1120700018780677. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Hip Int. 2018. PMID: 29998768 Review.
-
Effects of vitamin E incorporation in polyethylene on oxidative degradation, wear rates, immune response, and infections in total joint arthroplasty: a review of the current literature.Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1549-1557. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4237-8. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30470866 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Analysis of Wearing of Hip Joint Prostheses Composed of Different Contact Materials.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jul 7;14(14):3805. doi: 10.3390/ma14143805. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300724 Free PMC article.
-
Cup positioning and its effect on polyethylene wear of vitamin E- and non-vitamin E-supplemented liners in total hip arthroplasty: radiographic outcome at 5-year follow-up.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Mar;143(3):1679-1688. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04424-2. Epub 2022 Apr 10. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 35397656 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Endoprosthetic wear analysis using virtual CAD-based radiographs].Orthopade. 2018 Oct;47(10):811-819. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-3602-z. Orthopade. 2018. PMID: 30039467 Review. German.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials