Treatment of diaphyseal forearm fractures in children
- PMID: 25002936
- PMCID: PMC4083309
- DOI: 10.4081/or.2014.5325
Treatment of diaphyseal forearm fractures in children
Abstract
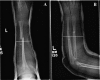
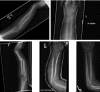
Both bone forearm fractures are common orthopedic injuries. Optimal treatment is dictated not only by fracture characteristics but also patient age. In the pediatric population, acceptable alignment can tolerate greater fracture displacement due to the bone's ability to remodel with remaining growth. Generally, these fractures can be successfully managed with closed reduction and casting, however operative fixation may also be required. The optimal method of fixation has not been clearly established. Currently, the most common operative interventions are open reduction with plate fixation versus closed or open reduction with intramedullary fixation. Plating has advantages of being more familiar to many surgeons, being theoretically superior in the ability to restore radial bow, and providing the possibility of hardware retention. Recently, intramedullary nailing has been gaining popularity due to decreased soft tissue dissection; however, a second operation is needed for hardware removal generally 6 months after the index procedure. Current literature has not established the superiority of one surgical method over the other. The goal of this manuscript is to review the current literature on the treatment of pediatric forearm fractures and provide clinical recommendations for optimal treatment, focusing specifically on children ages 3-10 years old.
Keywords: both-bone fractures; forearm fractures; pediatric; younger children.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng JC, Ng BK, Ying SY, Lam PK.A 10-year study of the changes in the pattern and treatment of 6,493 fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19:344-50 - PubMed
-
- Jones K, Weiner DS.The management of forearm fractures in children: a plea for conservatism. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19:811-5 - PubMed
-
- Flynn JM, Jones KJ, Garner MR, Goebel J.Eleven years experience in the operative management of pediatric forearm fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30:313-9 - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Paterson JM.A flexible intramedullary nails for fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:947-53 - PubMed
-
- Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prevot J.[Closed flexible medullary nailing in pediatric traumatology]. Chir Pediatr. 1983;24:383-5 [Article in French]. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

