Comparing cutaneous research funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases with 2010 Global Burden of Disease results
- PMID: 25003335
- PMCID: PMC4086973
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102122
Comparing cutaneous research funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases with 2010 Global Burden of Disease results
Abstract
Importance: Disease burden data helps guide research prioritization.
Objective: To determine the extent to which grants issued by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) reflect disease burden, measured by disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2010 project.
Design: Two investigators independently assessed 15 skin conditions studied by GBD 2010 in the NIAMS database for grants issued in 2013. The 15 skin diseases were matched to their respective DALYs from GBD 2010.
Setting: The United States NIAMS database and GBD 2010 skin condition disability data.
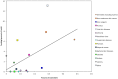
Main outcome(s) and measure(s): Relationship of NIAMS grant database topic funding with percent total GBD 2010 DALY and DALY rank for 15 skin conditions.
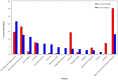
Results: During fiscal year 2013, 1,443 NIAMS grants were issued at a total value of $424 million. Of these grants, 17.7% covered skin topics. Of the total skin disease funding, 82% (91 grants) were categorized as "general cutaneous research." Psoriasis, leprosy, and "other skin and subcutaneous diseases" (ie; immunobullous disorders, vitiligo, and hidradenitis suppurativa) were over-represented when funding was compared with disability. Conversely, cellulitis, decubitus ulcer, urticaria, acne vulgaris, viral skin diseases, fungal skin diseases, scabies, and melanoma were under-represented. Conditions for which disability and funding appeared well-matched were dermatitis, squamous and basal cell carcinoma, pruritus, bacterial skin diseases, and alopecia areata.
Conclusions and relevance: Degree of representation in NIAMS is partly correlated with DALY metrics. Grant funding was well-matched with disability metrics for five of the 15 studied skin diseases, while two skin diseases were over-represented and seven were under-represented. Global burden estimates provide increasingly transparent and important information for investigating and prioritizing national research funding allocations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Murray C, Lopez A (2013) Measuring the Global Burden of Disease. NEJM 369 5: 448–57. - PubMed
-
- Reidpath DD, Allotey PA, Kouame A, Cummins RA (2003) Measuring health in a vacuum: examining the disability weight of the DALY. Health Policy Plan 18 4: 351–6. - PubMed
-
- Clavisi O, Bragge P, Tavender E, Turner T, Gruen R (2013) Effective stakeholder participation in setting research priorities using a Global Evidence Mapping approach. J Clin Epidemiol 66 5: 496–502. - PubMed
-
- Fleurence RL, Torgerson DJ (2004) Setting priorities for research. Health Policy 69 1: 1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

