Ruthenium complexes as NO donors for vascular relaxation induction
- PMID: 25004072
- PMCID: PMC6271244
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19079628
Ruthenium complexes as NO donors for vascular relaxation induction
Abstract
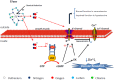
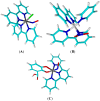
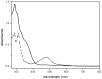
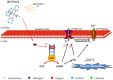
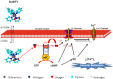
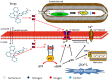
Nitric oxide (NO) donors are substances that can release NO. Vascular relaxation induction is among the several functions of NO, and the administration of NO donors is a pharmacological alternative to treat hypertension. This review will focus on the physicochemical description of ruthenium-derived NO donor complexes that release NO via reduction and light stimulation. In particular, we will discuss the complexes synthesized by our research group over the last ten years, and we will focus on the vasodilation and arterial pressure control elicited by these complexes. Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) and potassium channels are the main targets of the NO species released from the inorganic compounds. We will consider the importance of the chemical structure of the ruthenium complexes and their vascular effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
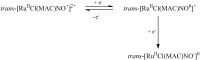
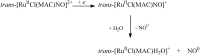
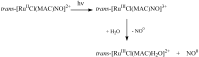
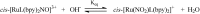
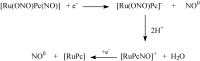
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

