Mitophagy switches cell death from apoptosis to necrosis in NSCLC cells treated with oncolytic measles virus
- PMID: 25004098
- PMCID: PMC4116530
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2028
Mitophagy switches cell death from apoptosis to necrosis in NSCLC cells treated with oncolytic measles virus
Abstract
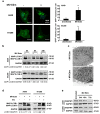
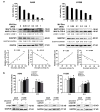
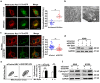
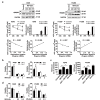
Although apoptotic phenomena have been observed in malignant cells infected by measles virus vaccine strain Edmonston B (MV-Edm), the precise oncolytic mechanisms are poorly defined. In this study we found that MV-Edm induced autophagy and sequestosome 1-mediated mitophagy leading to decreased cytochrome c release, which blocked the pro-apoptotic cascade in non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLCs). The decrease of apoptosis by mitophagy favored viral replication. Persistent viral replication sustained by autophagy ultimately resulted in necrotic cell death due to ATP depletion. Importantly, when autophagy was impaired in NSCLCs MV-Edm-induced cell death was significantly abrogated despite of increased apoptosis. Taken together, our results define a novel oncolytic mechanism by which mitophagy switches cell death from apoptosis to more efficient necrosis in NSCLCs following MV-Edm infection. This provides a foundation for future improvement of oncolytic virotherapy or antiviral therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a financial interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS, Golstein P, Green DR, Hengartner M, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Malorni W, Nunez G, et al. Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(1):3–11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duprez L, Wirawan E, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P. Major cell death pathways at a glance. Microbes Infect. 2009;11(13):1050–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

