Structure of Rhodococcus equi virulence-associated protein B (VapB) reveals an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel consisting of two Greek-key motifs
- PMID: 25005079
- PMCID: PMC4089522
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X14009911
Structure of Rhodococcus equi virulence-associated protein B (VapB) reveals an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel consisting of two Greek-key motifs
Abstract
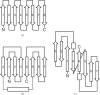
Members of the virulence-associated protein (Vap) family from the pathogen Rhodococcus equi regulate virulence in an unknown manner. They do not share recognizable sequence homology with any protein of known structure. VapB and VapA are normally associated with isolates from pigs and horses, respectively. To contribute to a molecular understanding of Vap function, the crystal structure of a protease-resistant VapB fragment was determined at 1.4 Å resolution. The structure was solved by SAD phasing employing the anomalous signal of one endogenous S atom and two bound Co ions with low occupancy. VapB is an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel with a single helix. Structural similarity to avidins suggests a potential binding function. Unlike other eight- or ten-stranded β-barrels found in avidins, bacterial outer membrane proteins, fatty-acid-binding proteins and lysozyme inhibitors, Vaps do not have a next-neighbour arrangement but consist of two Greek-key motifs with strand order 41238567, suggesting an unusual or even unique topology.
Keywords: Greek-key motif; Rhodococcus equi; Vap protein family; antiparallel β-barrel; single-wavelength anomalous dispersion.
Figures

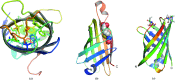
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
-
- von Bargen, K. & Haas, A. (2009). FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 33, 870–891. - PubMed
-
- DeLano, W. L. (2002). PyMOL http://www.pymol.org.
-
- Diederichs, K. & Karplus, P. A. (1997). Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 269–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

