Roles of elevated intravitreal IL-1β and IL-10 levels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 25005199
- PMCID: PMC4131322
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.136220
Roles of elevated intravitreal IL-1β and IL-10 levels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the roles of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in the vitreous of proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Materials and methods: Vitreous samples were obtained from 26 eyes of 26 patients with PDR and from eight eyes of eight cases without PDR. The IL-1β and IL-10 concentration in the vitreous was measured by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
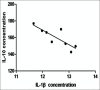
Results: Levels of IL-1β and IL-10 in vitreous were higher in PDR patients compared with control group. And there was significantly negative correlation between IL-1β and IL-10 in control group (r = -0.795; P = 0.032), whereas there was no significant correlation in PDR group (r = 0.176; P = 0.391).
Conclusion: Levels of IL-1β and IL-10 were upregulated in vitreous of PDR patients, and these two cytokines play roles in regulating the development and progression of PDR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Abu El-Asar AM, Al-Mezaine HS, Ola MS. Pathophysiology and management of diabetic retinopathy. Exp Rev Opthalmol. 2009;4:627–47.
-
- Koskela UE, Kuusisto SM, Nissinen AE, Savolainen MJ, Liinamaa MJ. High vitreous concentration of IL-6 and IL-8, but not of adhesion molecules in relation to plasma concentrations in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;49:108–14. - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Kim S, Park J, Lee HK, Park KS, Yu HG, et al. Differential expression of vitreous proteins in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2006;31:231–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical