Management of older or unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 25005246
- PMCID: PMC4289127
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2014.216
Management of older or unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is primarily a disease of older adults, for whom optimal treatment strategies remain controversial. Because of the concern for therapeutic resistance and, in particular, excessive toxicity or even treatment-related mortality, many older or medically unfit patients do not receive AML-directed therapy. Yet, evidence suggests that outcomes are improved if essentially all of these patients are offered AML therapy, ideally at a specialized cancer center. Medical fitness for tolerating intensive chemotherapy can be estimated relatively accurately with multiparameter assessment tools; this information should serve as basis for the assignment to intensive or non-intensive therapy. Until our accuracy in predicting the success of individual therapies improves, all patients should be considered for participation in a randomized controlled trial. Comparisons between individual trials will be facilitated once standardized, improved response criteria are developed, and standard treatment approaches have been defined against which novel therapies can be tested.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
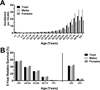
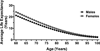
References
-
- Alibhai SMH, Leach M, Minden MD, Brandwein J. Outcomes and quality of care in acute myeloid leukemia over 40 years. Cancer. 2009;115(13):2903–2911. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AK. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: are we making progress? Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Juliusson G, Antunovic P, Derolf Å, Lehmann S, Möllgård L, Stockelberg D, et al. Age and acute myeloid leukemia: real world data on decision to treat and outcomes from the Swedish Acute Leukemia Registry. Blood. 2009;113(18):4179–4187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

