Early identification of brain injury in infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy at high risk for severe impairments: accuracy of MRI performed in the first days of life
- PMID: 25005267
- PMCID: PMC4113122
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-177
Early identification of brain injury in infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy at high risk for severe impairments: accuracy of MRI performed in the first days of life
Abstract
Background: Despite therapeutic hypothermia 30-70% of newborns with moderate or severe hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy will die or survive with significant long-term impairments. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the first days of life is being used for early identification of these infants and end of life decisions are relying more and more on it. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how MRI performed around day 4 of life correlates with the ones obtained in the second week of life in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) treated with hypothermia.
Methods: Prospective observational cohort study between April 2009 and July 2011. Consecutive newborns with HIE evaluated for therapeutic hypothermia were included. Two sequential MR studies were performed: an 'early' study around the 4th day of life and a 'late' study during the second week of life. MRI were assessed and scored by two neuroradiologists who were blinded to the clinical condition of the infants.
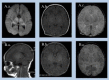
Results: Forty-eight MRI scans were obtained in the 40 newborns. Fifteen infants underwent two sequential MR scans. The localization, extension and severity of hypoxic-ischemic injury in early and late scans were highly correlated. Hypoxic-ischemic injury scores from conventional sequences (T1/T2) in the early MRI correlated with the scores of the late MRI (Spearman ρ = 0.940; p < .001) as did the scores between diffusion-weighted images in early scans and conventional images in late MR studies (Spearman ρ = 0.866; p < .001). There were no significant differences in MR images between the two sequential scans.
Conclusions: MRI in the first days of life may be a useful prognostic tool for clinicians and can help parents and neonatologist in medical decisions, as it highly depicts hypoxic-ischemic brain injury seen in scans performed around the second week of life.
Figures
References
-
- Gluckman PD, Wyatt JS, Azzopardi D, Ballard R, Edwards AD, Ferriero DM, Polin RA, Robertson CM, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A, Gunn AJ. Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365:663–670. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, Fanaroff AA, Poole WK, Wright LL, Higgins RD, Finer NN, Carlo WA, Duara S, Oh W, Cotten CM, Stevenson DK, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Guillet R, Jobe AH. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1574–1584. - PubMed
-
- Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday HL, Juszczak E, Kapellou O, Levene M, Marlow N, Porter E, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A, Brocklehurst P. TOBY Study Group. TOBY Study Group. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1349–1358. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs SE, Morley CJ, Inder TE, Stewart MJ, Smith KR, McNamara PJ, Wright IM, Kirpalani HM, Darlow BA, Doyle LW. Infant Cooling Evaluation Collaboration. Infant Cooling Evaluation Collaboration. Whole-body hypothermia for term and near-term newborns with hypoxicischemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2011;165:692–700. - PubMed
-
- Simbruner G, Mittal RA, Rohlmann F, Muche R. neo.nEURO.network trial participants. Systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: outcomes of neo-.nEURO.network RCT. Pediatrics. 2010;126:e771–e778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

