Cellular and physical mechanisms of branching morphogenesis
- PMID: 25005470
- PMCID: PMC4197615
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.104794
Cellular and physical mechanisms of branching morphogenesis
Abstract
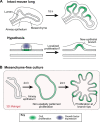
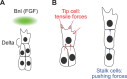
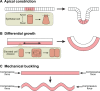
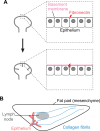
Branching morphogenesis is the developmental program that builds the ramified epithelial trees of various organs, including the airways of the lung, the collecting ducts of the kidney, and the ducts of the mammary and salivary glands. Even though the final geometries of epithelial trees are distinct, the molecular signaling pathways that control branching morphogenesis appear to be conserved across organs and species. However, despite this molecular homology, recent advances in cell lineage analysis and real-time imaging have uncovered surprising differences in the mechanisms that build these diverse tissues. Here, we review these studies and discuss the cellular and physical mechanisms that can contribute to branching morphogenesis.
Keywords: Bifurcation; Mechanical stress; Pattern; Proliferation; Tension.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Alcaraz J., Mori H., Ghajar C. M., Brownfield D., Galgoczy R., Bissell M. J. (2011). Collective epithelial cell invasion overcomes mechanical barriers of collagenous extracellular matrix by a narrow tube-like geometry and MMP14-dependent local softening. Integr. Biol. (Camb.) 3, 1153-1166. 10.1039/c1ib00073j - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alescio T., Colombo Piperno E. (1967). A quantitative assessment of mesenchymal contribution to epithelial growth rate in mouse embryonic lung developing in vitro. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 17, 213-227 - PubMed
-
- Alescio T., Di Michele M. (1968). Relationship of epithelial growth to mitotic rate in mouse embryonic lung developing in vitro. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 19, 227-237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

