Live cell integrated surface plasmon resonance biosensing approach to mimic the regulation of angiogenic switch upon anti-cancer drug exposure
- PMID: 25005895
- PMCID: PMC4372114
- DOI: 10.1021/ac402659j
Live cell integrated surface plasmon resonance biosensing approach to mimic the regulation of angiogenic switch upon anti-cancer drug exposure
Abstract
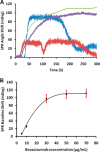
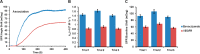
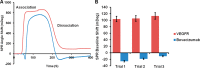
In this work, we report a novel surface plasmon resonance (SPR) based live-cell biosensing platform to measure and compare the binding affinity of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and VEGF to bevacizumab. Results have shown that bevacizumab binds VEGF with a higher association rate and affinity compared to VEGFR. Further, this platform has been employed to mimic the in vivo condition of the VEGF-VEGFR angiogenic switch. Competitive binding to VEGF between VEGFR and bevacizumab was monitored in real-time using this platform. Results demonstrated a significant blockage of VEGF-VEGFR binding by bevacizumab. From the results, it is evident that the proposed strategy is simple and highly sensitive for the direct and real-time measurements of bevacizumab drug efficacy to the VEGF-VEGFR angiogenic switch in living SKOV-3 cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a target of bevacizumab in cancer: from the biology to the clinic.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1845-57. doi: 10.2174/092986706777585059. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842197 Review.
-
Novel VEGF decoy receptor fusion protein conbercept targeting multiple VEGF isoforms provide remarkable anti-angiogenesis effect in vivo.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 12;8(8):e70544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070544. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23950958 Free PMC article.
-
VEGFA-VEGFR pathway blockade inhibits tumor-induced regulatory T-cell proliferation in colorectal cancer.Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):539-49. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2325. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23108136
-
Pharmacological characteristics and efficacy of a novel anti-angiogenic antibody FD006 in corneal neovascularization.BMC Biotechnol. 2014 Feb 27;14:17. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-17. BMC Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24575750 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibodies targeting vascular endothelial growth factor: current status and future challenges in cancer therapy.BioDrugs. 2009;23(5):289-304. doi: 10.2165/11317600-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2009. PMID: 19754219 Review.
Cited by
-
Application and Method of Surface Plasmon Resonance Technology in the Preparation and Characterization of Biomedical Nanoparticle Materials.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 11;19:7049-7069. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S468695. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39011388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ targeting TEM8 via immune response and polypeptide recognition by wavelength-modulated surface plasmon resonance biosensor.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 29;6:20006. doi: 10.1038/srep20006. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26822761 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing cancer cell metabolism for theranostic applications using metabolic glycoengineering of sialic acid in breast cancer as a pioneering example.Biomaterials. 2017 Feb;116:158-173. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.11.044. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 27926828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying Ligand-Protein Binding Kinetics with Self-Assembled Nano-oscillators.Anal Chem. 2019 Nov 5;91(21):14149-14156. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04195. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31593433 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient-deprived cancer cells preferentially use sialic acid to maintain cell surface glycosylation.Biomaterials. 2015 Nov;70:23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.08.020. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26295436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R.; Naishadham D.; Jemal A. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Reya T.; Morrison S. J.; Clarke M. F.; Weissman I. L. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. - PubMed
-
- Heng H. H. Q.; Stevens J. B.; Bremer S. W.; Ye K. J.; Liu G.; Ye C. J. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 109, 1072–1084. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A.; Allavena P.; Sica A.; Balkwill F. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

