A review of the systemic adverse effects of areca nut or betel nut
- PMID: 25006276
- PMCID: PMC4080659
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-5851.133702
A review of the systemic adverse effects of areca nut or betel nut
Abstract
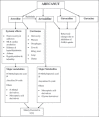
Areca nut is widely consumed by all ages groups in many parts of the world, especially south-east Asia. The objective of this review is to systematically review and collate all the published data that are related to the systemic effects of areca nut. The literature search was performed by an electronic search of the Pubmed and Cochrane databases using keywords and included articles published till October 2012. We selected studies that covered the effect of areca nut on metabolism, and a total of 62 studies met the criteria. There is substantial evidence for carcinogenicity of areca nut in cancers of the mouth and esophagus. Areca nut affects almost all organs of the human body, including the brain, heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and reproductive organs. It causes or aggravates pre-existing conditions such as neuronal injury, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, hepatotoxicity, asthma, central obesity, type II diabetes, hyperlipidemia, metabolic syndrome, etc. Areca nut affects the endocrine system, leading to hypothyroidism, prostate hyperplasia and infertility. It affects the immune system leading to suppression of T-cell activity and decreased release of cytokines. It has harmful effects on the fetus when used during pregnancy. Thus, areca nut is not a harmless substance as often perceived and proclaimed by the manufacturers of areca nut products such as Pan Masala, Supari Mix, Betel quid, etc. There is an urgent need to recognize areca nut as a harmful food substance by the policy makers and prohibit its glamorization as a mouth freshener. Strict laws are necessary to regulate the production of commercial preparations of areca nut.
Keywords: Adverse effects; areca nut; arecoline; betel nut; systemic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous