Incidence of BCR-ABL transcript variants in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: Their correlation with presenting features, risk scores and response to treatment with imatinib mesylate
- PMID: 25006280
- PMCID: PMC4080658
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-5851.133707
Incidence of BCR-ABL transcript variants in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: Their correlation with presenting features, risk scores and response to treatment with imatinib mesylate
Abstract
Context: The exact role of the different transcript variants of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and their impact on prognosis is yet to be definitely enumerated.
Aims: In this study, we have tried to correlate the presenting features, risk scores and treatment response with the BCR-ABL variants detected in our patients.
Settings and design: A cross-sectional unicentric hospital-based study on 80 patients diagnosed to have CML by bone marrow cytogenetics and confirmed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
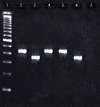
Materials and methods: RT-PCR for BCR-ABL was performed on consecutive patients with CML attending the CML clinic from January 2010 to December 2010. The medical charts of these patients were analyzed after a follow-up of 18 months in a retrospective manner.
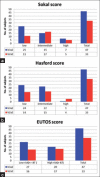
Statistical analysis: Box plot and histogram was used to see the distribution of variables. t-test was performed to enumerate the difference between risk scores in two populations of patients carrying two different BCR-ABL transcript variants.
Results: Nearly 56.25% of patients had b3a2 (e14a2) while 41.25% of patients showed b2a2 (e13a2) transcripts. The rest 2.5% (two patients) expressed the rare e19b2 variant. Patients with b2a2 presented with higher Sokal, Hasford and European Treatment and Outcomes Study score than their b3a2 counterpart. Different parameters such as the platelet count, leukocyte count, hemoglobin and splenomegaly showed a minor difference between the groups. More patients in the b2a2 group achieved complete hematologic response at 3 months, but it was not significant.
Conclusions: Patients with b2a2 variant CML tend to present with higher risk score, but do not behave in a vastly different manner than their b3a2 counterparts.
Keywords: BCR-ABL transcript variants; chronic myeloid leukemia; chronic myeloid leukemia risk scores; imatinib mesylate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nowell PC. The minute chromosome (Phl) in chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blut. 1962;8:65–6. - PubMed
-
- Ren R. Mechanisms of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:172–83. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Neriah Y, Daley GQ, Mes-Masson AM, Witte ON, Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986;233:212–4. - PubMed
-
- Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315:550–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

