Occupational hazard exposure and general health profile of welders in rural Delhi
- PMID: 25006312
- PMCID: PMC4083517
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5278.134953
Occupational hazard exposure and general health profile of welders in rural Delhi
Abstract
Background: Welding is a common industrial process associated with various health hazards. The aspect of duration of hazard exposure among welders at their workplace has been studied to limited extent in India.
Objective: To assess the duration of occupational hazard exposure and its association with symptoms among the welders.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted amongst 106 welders in North Delhi. Data was collected using a questionnaire containing items to assess the socio-demographic profile, their medical history and individual hazard exposure.
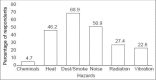
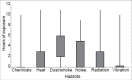
Results: Majority of them were involved in skilled/semi-skilled job (n = 99; 93%). The predominant nature of work for majority was manual. More than half reported their work to be physically hard (n = 56; 53%), involves much lifting of weight (n = 61; 57%), and is dangerous (n = 59; 56%). Dust/smoke followed by noise was reported to be most common hazards at the workplace by them. Most of them were suffering from eye related symptoms (n = 63; 59%) followed by skin conditions (n = 28; 26%). Skin diseases were reported to be significantly common among group of welders who were exposed to dust and radiation for ≥4 hours in a day (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Nearly half of the welders found their job to be dangerous and were being exposed to at least one hazardous substance at their workplace. Majority of them complained of eye symptoms. There is a need for health and safety training of this economically productive group.
Keywords: Health status; occupational exposures; welding; workplace.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Respiratory symptoms and spirometric abnormalities among welders in the welding workplace of the Indian unorganized sector.Work. 2021;69(3):885-894. doi: 10.3233/WOR-213521. Work. 2021. PMID: 34180459
-
Awareness of occupational hazards and utilization of safety measures among welders in Kaduna metropolis, northern Nigeria.Ann Afr Med. 2009 Jan-Mar;8(1):46-51. doi: 10.4103/1596-3519.55764. Ann Afr Med. 2009. PMID: 19763007
-
Awareness of occupational hazards and use of safety measures among welders: a cross-sectional study from Eastern Nepal.BMJ Open. 2014 Jun 2;4(6):e004646. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004646. BMJ Open. 2014. PMID: 24889850 Free PMC article.
-
Is electric arc welding linked to manganism or Parkinson's disease?Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(4):237-57. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524040-00004. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16499406 Review.
-
State-of-the-science review: Does manganese exposure during welding pose a neurological risk?J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2007 Nov-Dec;10(6):417-65. doi: 10.1080/15287390600975004. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2007. PMID: 17710609 Review.
Cited by
-
Occupational safety measures and morbidity among welders in Vellore, Southern India.Int J Occup Environ Health. 2016 Oct;22(4):300-306. doi: 10.1080/10773525.2016.1228287. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27682579 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth Analysis of Pattern of Occupational Injuries and Utilization of Safety Measures among Workers of Railway Wagon Repair Workshop in Jhansi (U.P.).Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2017 Sep-Dec;21(3):138-142. doi: 10.4103/ijoem.IJOEM_60_17. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2017. PMID: 29618914 Free PMC article.
-
Morbidity patterns among the welders of eastern Nepal: a cross-sectional study.Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016 Nov 15;28:62. doi: 10.1186/s40557-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016. PMID: 27891236 Free PMC article.
-
Personal protective eyewear usage among industrial workers in small-scale enterprises.Inj Epidemiol. 2020 Sep 22;7(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40621-020-00280-z. Inj Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32958044 Free PMC article.
-
A comment on "Occupational hazard exposure and general health profile of welders in rural Delhi".Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2014 Sep-Dec;18(3):162. doi: 10.4103/0019-5278.146918. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2014. PMID: 25598624 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kumara JT. Aruna College of Nursing. Karnataka: Rajiv Gandhi University of health Sciences; A Study to assess the effectiveness of Self Instructional Module (SIM) on the awareness of selected Occupational Hazards and its Prevention among Welders at selected Workshops in Tumkur District [Unpublished Dissertation]
-
- Gulani KK. 1st ed. Delhi: Kumar Publishing House; 2008. Principles and practice of community health nursing; pp. 508–9.
-
- A vision for all. Geneva: WHO; 1998. World Health Organization (WHO). The World Health Report 1998-Life in the 21st century; pp. 5–6.
-
- Sabitu K, Iliyasu Z, Dauda MM. Awareness of occupational hazards and utilization of safety measures among welders in kaduna metropolis, Northern Nigeria. Ann Afr Med. 2009;8:46–51. - PubMed
-
- Shaikh TQ, Bhojani FA. Occupational injuries and perceptions of hazards among road-side welding workers. J Pak Med Assoc. 1991;41:187–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources