Optimal precurarizing dose of rocuronium to decrease fasciculation and myalgia following succinylcholine administration
- PMID: 25006369
- PMCID: PMC4085266
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.6.451
Optimal precurarizing dose of rocuronium to decrease fasciculation and myalgia following succinylcholine administration
Abstract
Background: Succinylcholine commonly produces frequent adverse effects, including muscle fasciculation and myalgia. The current study identified the optimal dose of rocuronium to prevent succinylcholine-induced fasciculation and myalgia and evaluated the influence of rocuronium on the speed of onset produced by succinylcholine.
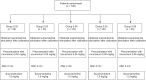
Methods: This randomized, double-blinded study was conducted in 100 patients randomly allocated into five groups of 20 patients each. Patients were randomized to receive 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05 and 0.06 mg/kg rocuronium as a precurarizing dose. Neuromuscular monitoring after each precurarizing dose was recorded from the adductor pollicis muscle using acceleromyography with train-of-four stimulation of the ulnar nerve. All patients received succinylcholine 1.5 mg/kg at 2 minutes after the precurarization, and were assessed the incidence and severity of fasciculations, while myalgia was assessed at 24 hours after surgery.
Results: The incidence and severity of visible muscle fasciculation was significantly less with increasing the amount of precurarizing dose of rocuronium (P < 0.001). Those of myalgia tend to decrease according to increasing the amount of precurarizing dose of rocuronium, but there was no significance (P = 0.072). The onset time of succinylcholine was significantly longer with increasing the amount of precurarizing dose of rocuronium (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Precurarization with 0.04 mg/kg rocuronium was the optimal dose considering the reduction in the incidence and severity of fasciculation and myalgia with acceptable onset time, and the safe and effective precurarization.
Keywords: Fasciculation; Myalgia; Neuromuscular blockade; Precurarization; Rocuronium; Succinylcholine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A randomized trial to identify optimal precurarizing dose of rocuronium to avoid precurarization-induced neuromuscular block.J Anesth. 2011 Apr;25(2):200-4. doi: 10.1007/s00540-010-1086-z. Epub 2011 Jan 12. J Anesth. 2011. PMID: 21225293 Clinical Trial.
-
[Precurarization with rocuronium prevents fasciculations and biochemical changes after succinylcholine administration].Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2004 Apr;51(4):184-9. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2004. PMID: 15168925 Clinical Trial. Spanish.
-
A rapid precurarization technique using rocuronium.Can J Anaesth. 1998 May;45(5 Pt 1):397-401. doi: 10.1007/BF03012573. Can J Anaesth. 1998. PMID: 9598252 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of rocuronium and d-tubocurarine for prevention of succinylcholine-induced fasciculations and myalgia.Can J Anaesth. 1997 Nov;44(11):1144-7. doi: 10.1007/BF03013334. Can J Anaesth. 1997. PMID: 9398951 Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative pregabalin prevents succinylcholine-induced fasciculation and myalgia: A meta-analysis of randomized trials.Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2024 Apr;71(4):324-331. doi: 10.1016/j.redare.2022.12.002. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 37673208
Cited by
-
Comparison of perioperative outcomes between pure laparoscopic surgery and open right hepatectomy in living donor hepatectomy: Propensity score matching analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 24;10(1):5314. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62289-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32210359 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Non-depolarizing Muscle Relaxants Rocuronium Versus Vecuronium in the Assessment of Post-Succinylcholine Complications in Surgeries Under General Anesthesia: A Randomized Double-Blind Study at a Tertiary Care Hospital.Cureus. 2021 Nov 21;13(11):e19793. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19793. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34820250 Free PMC article.
-
Critical biomechanical and clinical insights concerning tissue protection when positioning patients in the operating room: A scoping review.Int Wound J. 2020 Oct;17(5):1405-1423. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13408. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Int Wound J. 2020. PMID: 32496025 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of low-dose ketamine on succinylcholine-induced postoperative myalgia in outpatient surgeries: a randomized, double-blind study.J Pain Res. 2016 Jul 6;9:503-8. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S106576. eCollection 2016. J Pain Res. 2016. PMID: 27462175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morris J, Cook TM. Rapid sequence induction: a national survey of practice. Anaesthesia. 2001;56:1090–1097. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Jeon SY, Cho H, Lee HW, Lom HJ, Chang SH, et al. Rocuronium pretreatment for prevention of myalgia following succinylcholine administration. Korean J Anesthesiol. 1999;36:777–782.
-
- Schreiber JU, Lysakowski C, Fuchs-Buder T, Tramèr MR. Prevention of succinylcholine-induced fasciculation and myalgia: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Anesthesiology. 2005;103:877–884. - PubMed
-
- Kopman AF, Khan NA, Neuman GG. Precurarization and priming: a theoretical analysis of safety and timing. Anesth Analg. 2001;93:1253–1256. - PubMed
-
- Mencke T, Schreiber JU, Becker C, Bolte M, Fuchs-Buder T. Pretreatment before succinylcholine for outpatient anesthesia? Anesth Analg. 2002;94:573–576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

