PK10453, a nonselective platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor, prevents the progression of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 25006424
- PMCID: PMC4070754
- DOI: 10.1086/674881
PK10453, a nonselective platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor, prevents the progression of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
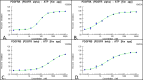
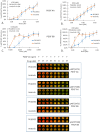
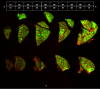
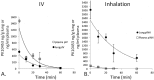
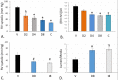
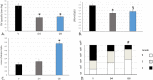
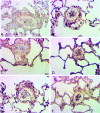
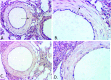
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling pathway has been found to be activated in human pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and in animal models of the disease. Our study tested the hypothesis that a novel, nonselective inhaled PDGF receptor inhibitor, PK10453, would decrease pulmonary hypertension both in the rat monocrotaline (MCT) model and the rat MCT plus pneumonectomy (MCT+PN) model of PAH. PK10453, delivered by inhalation for 4 (D4)- and 8 (D8)-minute exposures 3 times a day for 2 weeks, decreased right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) in both the rat MCT and rat MCT+PN models: RVSP was 80.4 ± 2.6 mmHg in the vehicle MCT group (n = 6), 44.4 ± 5.8 mmHg in the D4 MCT group (n = 6), and 37.1 ± 4.5 mmHg in the D8 MCT group (n = 5; P < 0.001 vs. vehicle); RVSP was 75.7 ± 7.1 mmHg in the vehicle MCT+PN group (n = 9), 40.4 ± 2.7 mmHg in the D4 MCT+PN group (n = 10), and 43.0 ± 3.0 mmHg in the D8 MCT+PN group (n = 8; P < 0.001). In the rat MCT+PN model, continuous telemetry monitoring of pulmonary artery pressures also demonstrated that PK10453 prevented the progression of PAH. Imatinib given by inhalation was equally effective in the MCT model but was not effective in the MCT+PN model. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated increased activation of the PDGFβ receptor compared to the PDGFα receptor in neointimal and perivascular lesions found in the MCT+PN model. We show that imatinib is selective for the PDGFα receptor, whereas PK10453 has a lower half-maximal inhibitor concentration (IC50) for inhibition of kinase activity of both the PDGFα and PDGFβ receptors compared to imatinib. In conclusion, PK10453, when delivered by inhalation, significantly decreased the progression of PAH in the rat MCT and MCT+PN models. Nonselective inhibition of both the PDGFα and PDGFβ receptors may have a therapeutic advantage over selective PDGFα receptor inhibition in PAH.
Keywords: kinase inhibitors; platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Figures



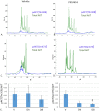
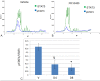
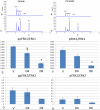
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Shp2 ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats.BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Aug 7;18(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0700-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 30086741 Free PMC article.
-
Development of occlusive neointimal lesions in distal pulmonary arteries of endothelin B receptor-deficient rats: a new model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circulation. 2005 Jun 7;111(22):2988-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.491456. Epub 2005 May 31. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15927975 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats by suppressing the ERK/MAPK pathway.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39(1):34-41. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2016.1210620. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28055284
-
Transection of the cervical sympathetic trunk inhibits the progression of pulmonary arterial hypertension via ERK-1/2 Signalling.Respir Res. 2019 Jun 14;20(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1090-2. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31200778 Free PMC article.
-
[Tanshinone IIA sulfonate upregulated pulmonary artery smooth muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ expression in monocrotaline induced pulmonary hypertension rat].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014 May;37(5):360-4. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25011512 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Galectin-3 Promotes ROS, Inflammation, and Vascular Fibrosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1303:13-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63046-1_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33788185
-
Current Overview of the Biology and Pharmacology in Sugen/Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2024 Oct;37(5):241-283. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2024.0016. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39388691 Review.
-
Phosphoproteomic analysis of lung tissue from patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Pulm Circ. 2021 Aug 19;11(3):20458940211031109. doi: 10.1177/20458940211031109. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. Pulm Circ. 2021. PMID: 34966541 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for Old and New Small-Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors as Effective Treatments in Pulmonary Hypertension-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12858. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312858. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684570 Free PMC article.
-
Positioning imatinib for pulmonary arterial hypertension: A phase I/II design comprising dose finding and single-arm efficacy.Pulm Circ. 2021 Oct 17;11(4):20458940211052823. doi: 10.1177/20458940211052823. eCollection 2021 Oct-Dec. Pulm Circ. 2021. PMID: 34868551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perros F, Montani D, Dorfmüller P, Durand-Gasselin I, Tcherakian C, Le Pavec J, Mazmanian M, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor expression and function in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;178:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Ghofrani HA, Seeger W, Grimminger F. Imatinib for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1412–1413. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Barst RJ, Bourge RC, Feldman J, Frost AE, Galiè N, Gómez-Sánchez MA, et al. Imatinib mesylate as add-on therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: results of the randomized IMPRES study. Circulation 2013;127:1128–1138. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

