The serine-threonine phosphatase calcineurin is a regulator of endothelial store-operated calcium entry
- PMID: 25006427
- PMCID: PMC4070751
- DOI: 10.1086/675641
The serine-threonine phosphatase calcineurin is a regulator of endothelial store-operated calcium entry
Abstract
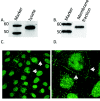
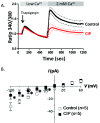
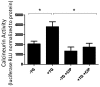
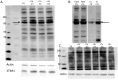
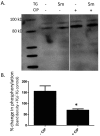
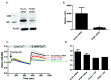
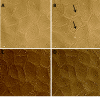
Disruption of the endothelium leads to increased permeability, allowing extravasation of macromolecules and other solutes from blood vessels. Calcium entry through a calcium-selective, store-operated calcium (SOC) channel, I soc, contributes to barrier disruption. An understanding of the mechanisms surrounding the regulation of I soc is far from complete. We show that the calcium/calmodulin-activated phosphatase calcineurin (CN) plays a role in regulation of SOC entry, possibly through the dephosphorylation of stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1). Phosphorylation has been implicated as a regulatory mechanism of activity for a number of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) and SOC channels, including I soc. Our results show that STIM1 phosphorylation increases in pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs) upon activation of SOC entry. However, the phosphatases involved in STIM1 dephosphorylation are unknown. We found that a CN inhibitor (calcineurin inhibitory peptide [CIP]) increases the phosphorylation pattern of STIM1. Using a fura 2-acetoxymethyl ester approach to measure cytosolic calcium in PAECs, we found that CIP decreases SOC entry following thapsigargin treatment in PAECs. Luciferase assays indicate that thapsigargin induces activation of CN activity and confirm inhibition of CN activity by CIP in PAECs. Also, I soc is significantly attenuated in whole-cell patch-clamp studies of PAECs treated with CIP. Finally, PAECs pretreated with CIP exhibit decreased interendothelial cell gap formation in response to thapsigargin-induced SOC entry, as compared to control cells. Taken together, our data show that CN contributes to the phosphorylation status of STIM1, which is important in regulation of endothelial SOC entry and I soc activity.
Keywords: Isoc; STIM1; TRPC; phosphatase; phosphorylation; stromal interaction molecule 1; transient receptor potential.
Figures
References
-
- Parekh AB, Putney JW Jr. Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev 2005;85:757–810. - PubMed
-
- Cioffi DL, Wu S, Stevens T. Transient receptor potential cation channels and store-operated Ca2+ channels. In: Yuan JX-J, ed. Ion channels in pulmonary vasculature. Lung Biology in Health and Disease, no. 197. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis, 2005:125–146.
-
- Wu S, Cioffi EA, Alvarez D, Sayner SL, Chen H, Cioffi DL, King J, et al. Essential role of a Ca2+-selective, store-operated current (ISOC) in endothelial cell permeability: determinants of the vascular leak site. Circ Res 2005;96:856–863. - PubMed
-
- Brough GH, Wu S, Cioffi D, Moore TM, Li M, Dean N, Stevens T. Contribution of endogenously expressed Trp1 to a Ca2+-selective, store-operated Ca2+ entry pathway. FASEB J 2001;15:1727–1738. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

