Loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator impairs lung endothelial cell barrier function and increases susceptibility to microvascular damage from cigarette smoke
- PMID: 25006445
- PMCID: PMC4070785
- DOI: 10.1086/675989
Loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator impairs lung endothelial cell barrier function and increases susceptibility to microvascular damage from cigarette smoke
Abstract
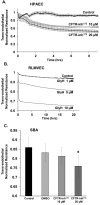
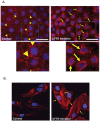
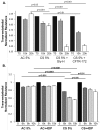
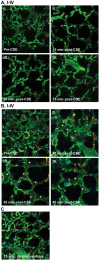
Abnormal lung microvascular endothelial vascular barrier function may contribute to pulmonary inflammation, such as that occurring during inhalation of cigarette smoke (CS). Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), an anion channel expressed in both epithelial and endothelial cells, regulates the organization of tight junctions between epithelial cells and has also been implicated in the transport of sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P), a vascular barrier-enhancing sphingolipid. Because CS has been shown to affect CFTR function, we hypothesized that CFTR function contributes to lung endothelial cell barrier and that CFTR dysfunction worsens CS-induced injury. CFTR inhibitors GlyH-101 or CFTRinh172 caused a dose-dependent increase in pulmonary or bronchial endothelial monolayer permeability, which peaked after 4 hours. CFTR inhibition was associated with both intercellular gaps and actin stress fiber formation compared with vehicle-treated cells. Increasing endothelial S1P, either by exogenous treatment or by inhibition of its degradation, significantly improved the barrier function in CFTR-inhibited monolayers. Both cultured lung endothelia and the lung microcirculation visualized in vivo with intravital two-photon imaging of transgenic mice deficient in CFTR showed that CFTR dysfunction increased susceptibility to CS-induced permeability. These results suggested that CFTR function might be required for lung endothelial barrier, including adherence junction stability. Loss of CFTR function, especially concomitant to CS exposure, might promote lung inflammation by increasing endothelial cell permeability, which could be ameliorated by S1P.
Keywords: COPD; S1P; ceramides; cystic fibrosis; sphingolipids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CFTR regulation of intracellular pH and ceramides is required for lung endothelial cell apoptosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;41(3):314-23. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0264OC. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19168702 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of sphingosine kinase 2 attenuates cigarette smoke-mediated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-like symptoms by reducing lung inflammation.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Mar 16;23(2):259-270. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.8034. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36226596 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of lung endothelial barrier disruption induced by cigarette smoke: role of oxidative stress and ceramides.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):L836-46. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00385.2010. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21873444 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette Smoke-Induced Acquired Dysfunction of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 23;2018:6567578. doi: 10.1155/2018/6567578. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29849907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cigarette smoke and CFTR: implications in the pathogenesis of COPD.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Oct 15;305(8):L530-41. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00039.2013. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23934925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) in Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells Controls Oxidative Stress, Reactive Oxygen-Mediated Cell Signaling and Inflammatory Responses.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 29;11:879. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00879. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848840 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide and Regulation of Vascular Tone.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 18;20(2):411. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020411. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-emerging regulator of cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 May;75(10):1737-1756. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2755-6. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29411041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravital Imaging of Pulmonary Immune Response in Inflammation and Infection.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 15;8:620471. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.620471. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33520993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characteristics and Treatment of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with COPD: A Review Article.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 4;20(18):4329. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184329. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31487864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Teichgraber V, Ulrich M, Endlich N, et al. Ceramide accumulation mediates inflammation, cell death and infection susceptibility in cystic fibrosis. Nat Med 2008;14:382–391. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

