Does Postevacuation β -Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Level Predict the Persistent Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia?
- PMID: 25006482
- PMCID: PMC4076647
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/494695
Does Postevacuation β -Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Level Predict the Persistent Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia?
Abstract
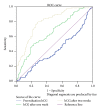
β -human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) level is not a reliable marker for early identification of persistent gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) after evacuation of hydatidiform mole. Thus, this study was conducted to evaluate β -HCG regression after evacuation as a predictive factor of malignant GTN in complete molar pregnancy. Methods. In this cross-sectional study, we evaluated a total of 260 patients with complete molar pregnancy. Sixteen of the 260 patients were excluded. Serum levels of HCG were measured in all patients before treatment and after evacuation. HCG level was measured weekly until it reached a level lower than 5 mIU/mL. Results. The only predictors of persistent GTN are HCG levels one and two weeks after evacuation. The cut-off point for the preevacuation HCG level was 6000 mIU/mL (area under the curve, AUC, 0.58; sensitivity, 38.53%; specificity, 77.4%), whereas cut-off points for HCG levels one and two weeks after evacuation were 6288 mIU/mL (AUC, 0.63; sensitivity, 50.46%; specificity, 77.0%) and 801 mIU/mL (AUC, 0.80; sensitivity, 79.82%; specificity, 71.64%), respectively. Conclusion. The rate of decrease of HCG level at two weeks after surgical evacuation is the most reliable and strongest predictive factor for the progression of molar pregnancies to persistent GTN.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined analysis of clinical features, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) value, and hCG ratios for early prediction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Apr;307(4):1145-1154. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06785-w. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36116082
-
Prediction of persistent gestational trophobalstic neoplasia: the role of hCG level and ratio in 2 weeks after evacuation of complete mole.Gynecol Oncol. 2012 Feb;124(2):250-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.10.035. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Gynecol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22094931
-
Postevacuation hCG levels and risk of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia in women with complete molar pregnancy.Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Sep;106(3):548-52. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000174583.51617.25. Obstet Gynecol. 2005. PMID: 16135585
-
Does a human chorionic gonadotropin level of over 20,000 IU/L four weeks after uterine evacuation for complete hydatidiform mole constitute an indication for chemotherapy for gestational trophoblastic neoplasia?Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 Apr;223:50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018. PMID: 29477553 Review.
-
Current management of gestational trophoblastic diseases.Gynecol Oncol. 2009 Mar;112(3):654-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.09.005. Epub 2008 Oct 12. Gynecol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18851873 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Detection of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia Based on Serial Measurement of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Hormone in Women with Molar Pregnancy.Int J Prev Med. 2020 Dec 11;11:187. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_288_19. eCollection 2020. Int J Prev Med. 2020. PMID: 33815711 Free PMC article.
-
Serum human chorionic gonadotropin ratios for the detection of etoposide, methotrexate, dactinomycin, cyclophosphamide, and vincristine resistance in high-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 20;5(4):e729. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.729. eCollection 2022 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35873390 Free PMC article.
-
A tutorial on dynamic risk prediction of a binary outcome based on a longitudinal biomarker.Biom J. 2020 Mar;62(2):398-413. doi: 10.1002/bimj.201900044. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Biom J. 2020. PMID: 31777998 Free PMC article.
-
Ten-Year Review of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease at Lady Reading Hospital, Peshawar.Cureus. 2022 Jul 6;14(7):e26620. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26620. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35936190 Free PMC article.
-
Combined analysis of clinical features, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) value, and hCG ratios for early prediction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Apr;307(4):1145-1154. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06785-w. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36116082
References
-
- Kang WD, Choi HS, Kim SM. Prediction of persistent gestational trophobalstic neoplasia: the role of hCG level and ratio in 2 weeks after evacuation of complete mole. Gynecologic Oncology. 2012;124(2):250–253. - PubMed
-
- Monchek R, Wiedaseck S. Gestational trophoblastic disease: an overview. Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health. 2012;57(3):255–259. - PubMed
-
- Seki K, Matsui H, Sekiya S. Advances in the clinical laboratory detection of gestational trophoblastic disease. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2004;349(1-2):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Alazzam M, Tidy J, Hancock BW, Osborne R. First line chemotherapy in low risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009;(1)CD007102 - PubMed
-
- Khoo S-K, Baartz D, Sidhu M, Yip W-L, Tripcony L. Analysis of risk factors for persistent gestational trophoblastic disease. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2009;49(6):657–659. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources