Conceptuation, formulation and evaluation of sustained release floating tablets of captopril compression coated with gastric dispersible hydrochlorothiazide using 2(3) factorial design
- PMID: 25006552
- PMCID: PMC4083537
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-973X.133055
Conceptuation, formulation and evaluation of sustained release floating tablets of captopril compression coated with gastric dispersible hydrochlorothiazide using 2(3) factorial design
Abstract
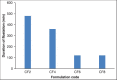
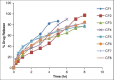
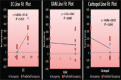
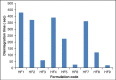
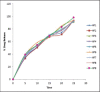
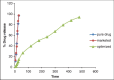
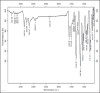
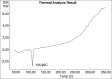
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is regarded as the gold standard for hypertensive therapy in non-dipping hypertension patients. A novel compression coated formulation of captopril and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) was developed in order to improve the efficacy of antihypertensive therapy considering the half-life of both drugs. The synergistic action using combination therapy can be effectively achieved by sustained release captopril (t1/2= 2.5 h) and fast releasing HCTZ (average t1/2= 9.5 h). The sustained release floating tablets of captopril were prepared by using 2(3) factorial design by employing three polymers i.e., ethyl cellulose (EC), carbopol and xanthan gum at two levels. The formulations (CF1-CF8) were optimized using analysis of variance for two response variables, buoyancy and T50%. Among the three polymers employed, the coefficients and P values for the response variable buoyancy and T50% using EC were found to be 3.824, 0.028 and 0.0196, 0.046 respectively. From the coefficients and P values for the two response variables, formulation CF2 was optimized, which contains EC polymer alone at a high level. The CF2 formulation was further compression coated with optimized gastric dispersible HCTZ layer (HF9). The compression coated tablet was further evaluated using drug release kinetics. The Q value of HCTZ layer is achieved within 20 min following first order release whereas the Q value of captopril was obtained at 6.5 h following Higuchi model, from which it is proved that rapid release HCTZ and slow release of captopril is achieved. The mechanism of drug release was analyzed using Peppas equation, which showed an n >0.90 confirming case II transportation mechanism for drug release.
Keywords: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; analysis of variance; compression coating; ethyl cellulose; floating drug delivery; non-dipping.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Tsioufis C, Andrikou I, Thomopoulos C, Petras D, Manolis A, Stefanadis C. Comparative prognostic role of nighttime blood pressure and nondipping profile on renal outcomes. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33:277–88. - PubMed
-
- Hansen TW, Li Y, Boggia J, Thijs L, Richart T, Staessen JA. Predictive role of the nighttime blood pressure. Hypertension. 2011;57:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Frank J. Managing hypertension using combination therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:1279–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

