Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension and interstitial lung diseases
- PMID: 25006558
- PMCID: PMC4083524
- DOI: 10.4103/1947-2714.134368
Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension and interstitial lung diseases
Abstract
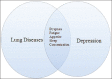
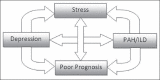
Advanced lung diseases such as pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and interstitial lung diseases (ILD) are chronic diseases that cause significantly high morbidity and mortality. As a result, patients can undergo some psychological changes leading to a poor quality of life and depression. Diagnosis of depression is often obscured because fatigue and apathy, two common symptoms of depression, frequently overlap with PAH and ILD. Healthcare providers are sometimes reluctant to ask or mistakenly believe that these symptoms are part of the ongoing disease process, rather than a serious condition like depression. Screening tools are available for physicians to be well positioned in recognizing clinical depression in PAH and ILD. A MedLine/PubMED search was performed identifying all relevant articles with "PAH", "ILD", "screening tools" and/or "Depression" in the title. The aim of this review is to provide a brief description of some of the instruments used to screen patients and classes of psychotropic medications accessible to physicians. While pulmonary rehabilitation programs can have a positive impact on patients, physicians should also utilize cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) as part of regular care.
Keywords: Depression; Interstitial lung diseases; Medications; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Screening tools.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension: An undertreated comorbidity.Lung India. 2016 Jan-Feb;33(1):58-63. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.173072. Lung India. 2016. PMID: 26933309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemodynamic Response to Treatment and Outcomes in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Interstitial Lung Disease Versus Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis: Data From a Study Identifying Prognostic Factors in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Interstitial Lung Disease.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;73(2):295-304. doi: 10.1002/art.41512. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32892515
-
Interstitial lung disease increases mortality in systemic sclerosis patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension without affecting hemodynamics and exercise capacity.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Feb;36(2):381-390. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3504-6. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28028682
-
Mortality and hospitalization outcomes of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary hypertension in the Singapore systemic sclerosis cohort.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Jun;50(3):473-479. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 31810742
-
Evaluation and management approaches for scleroderma lung disease.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2017 Aug;11(8):327-340. doi: 10.1177/1753465817713680. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2017. PMID: 28621173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension: An undertreated comorbidity.Lung India. 2016 Jan-Feb;33(1):58-63. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.173072. Lung India. 2016. PMID: 26933309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease: An Exploratory Review on Molecular Mechanisms.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(6):618-633. doi: 10.2174/1389557523666230816090112. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37587813 Review.
-
Symptom severity and its effect on health-related quality of life over time in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a multisite longitudinal cohort study.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2018 Mar 1;5(1):e000263. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000263. eCollection 2018. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29531745 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation and exercise in pulmonary arterial hypertension: An underutilized intervention.J Exerc Rehabil. 2015 Apr 30;11(2):74-9. doi: 10.12965/jer.150190. eCollection 2015 Apr. J Exerc Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 25960979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary arterial hypertension: the burden of disease and impact on quality of life.Eur Respir Rev. 2015 Dec;24(138):621-9. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0063-2015. Eur Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 26621976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Ridder D, Geenen R, Kuijer R, van Middendorp H. Psychological adjustment to chronic disease. Lancet. 2008;372:246–55. - PubMed
-
- Shanmugam G, Bhutani S, Khan DA, Brown ES. Psychiatric considerations in pulmonary disease. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2007;30:761–80. - PubMed
-
- Ain A, Lolak S. Psychiatric aspects of chronic lung disease. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009;11:219–25. - PubMed
-
- Text Revision. 4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders.
-
- Belmaker RH, Agam G. Major depressive disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:55–68. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

