Competitive HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors Show Protection against Oxidative Stress by a Mechanism Partially Dependent on Glycolysis
- PMID: 25006572
- PMCID: PMC4061615
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/598587
Competitive HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors Show Protection against Oxidative Stress by a Mechanism Partially Dependent on Glycolysis
Abstract
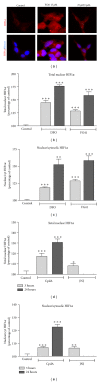
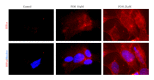
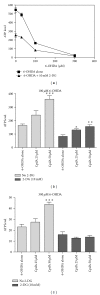
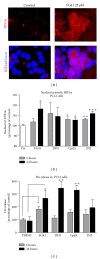
The hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a central transcription factor involved in the cellular and molecular adaptation to hypoxia and low glucose supply. The level of HIF-1 is to a large degree regulated by the HIF prolyl hydroxylase enzymes (HPHs) belonging to the Fe(II) and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily. In the present study, we compared competitive and noncompetitive HPH-inhibitor compounds in two different cell types (SH-SY5Y and PC12). Although the competitive HPH-inhibitor compounds were found to be pharmacologically more potent than the non-competitive compounds at inhibiting HPH2 and HPH1, this was not translated into the cellular effects of the compounds, where the non-competitive inhibitors were actually more potent than the competitive in stabilizing and translocatingHIF1 α to the nucleus (quantified with Cellomics ArrayScan technology). This could be explained by the high cellular concentrations of the cofactor 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) as the competitive inhibitors act by binding to the 2-OG site of the HPH enzymes. Both competitive and non-competitive HPH inhibitors protected the cells against 6-OHDA induced oxidative stress. In addition, the protective effect of a specific HPH inhibitor was partially preserved when the cells were serum starved and exposed to 2-deoxyglucose, an inhibitor of glycolysis, indicating that other processes than restoring energy supply could be important for the HIF-mediated cytoprotection.
Figures


References
-
- Kaelin WG, Jr., Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Molecular Cell. 2008;30(4):393–402. - PubMed
-
- Epstein ACR, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, et al. C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell. 2001;107(1):43–54. - PubMed
-
- Sridharan V, Guichard J, Bailey RM, Kasiganesan H, Beeson C, Wright GL. The prolyl hydroxylase oxygen-sensing pathway is cytoprotective and allows maintenance of mitochondrial membrane potential during metabolic inhibition. American Journal of Physiology—Cell Physiology. 2007;292(2):C719–C728. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
