Vitamin status as a determinant of serum homocysteine concentration in type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 25006590
- PMCID: PMC4071945
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/807209
Vitamin status as a determinant of serum homocysteine concentration in type 2 diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
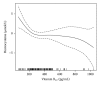
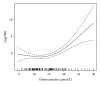
We investigated the association of serum homocysteine levels and vitamin status with type 2 diabetic retinopathy. This study included 65 patients with and 75 patients without diabetic retinopathy. Patients with diabetic retinopathy had significantly higher serum homocysteine levels (P < 0.001), higher prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia (P < 0.001), lower serum folic acid (P < 0.001), and vitamin B12 (P = 0.014) levels than those without diabetic retinopathy. Regression analysis revealed that homocysteine was an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy and there was a threshold in its serum level (13.7 μ mol/L), above which the risk of diabetic retinopathy greatly increases (OR = 1.66, P = 0.001). Folic acid was associated with decreased odds for diabetic retinopathy (OR = 0.73, P < 0.001). There was a threshold in serum vitamin B12 level (248.4 pg/mL), below which serum homocysteine concentration significantly increases with decreasing serum vitamin B12 (P = 0.003). Our findings suggest that hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor for the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Decreased serum levels of folic acid and vitamin B12, through raising serum homocysteine concentrations, may also affect the diabetic retinopathy risk.
Figures
References
-
- Humphrey LL, Fu R, Rogers K, Freeman M, Helfand M. Homocysteine level and coronary heart disease incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2008;83(11):1203–1212. - PubMed
-
- Homocysteine Studies Collaboration. Homocysteine and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: a meta-analysis. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;288(16):2015–2022. - PubMed
-
- Khandanpour N, Loke YK, Meyer FJ, Jennings B, Armon MP. Homocysteine and peripheral arterial disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2009;38(3):316–322. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(supplement 1):564–571.
-
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs—an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology. 1991;98(supplement 5):786–806. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials