Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of immobilized thermophilic esterase on hydrophobic macroporous resin for application in poly(ε-caprolactone) synthesis
- PMID: 25006789
- PMCID: PMC6270815
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19079838
Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of immobilized thermophilic esterase on hydrophobic macroporous resin for application in poly(ε-caprolactone) synthesis
Abstract
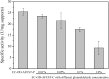
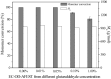
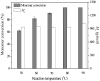
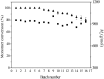
The immobilized thermophilic esterase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus was successfully constructed through the glutaraldehyde-mediated covalent coupling after its physical adsorption on a hydrophobic macroporous resin, Sepabeads EC-OD. Through 0.05% glutaraldehyde treatment, the prevention of enzyme leaching and the maintenance of catalytic activity could be simultaneously realized. Using the enzymatic ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone as a model, effects of organic solvents and reaction temperature on the monomer conversion and product molecular weight were systematically investigated. After the optimization of reaction conditions, products were obtained with 100% monomer conversion and Mn values lower than 1010 g/mol. Furthermore, the cross‑linked immobilized thermophilic esterase exhibited an excellent operational stability, with monomer conversion values exceeding 90% over the course of 12 batch reactions, still more than 80% after 16 batch reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang Y., Yu Y., Zhang Y., Liu C., Shi W., Li Q. Lipase/esterase-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization: A green polymer synthesis technique. Process Biochem. 2011;46:1900–1908. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2011.07.016. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

